Euclidean Algorithm
Computer science is (almost by definition) a science about computers -- a device first conceptualized in the 1800's. Computers have become so revolutionary, that it is difficult to think of our lives today without them. That said, algorithms are much older and have existed in the world for millennia. Incredibly, a few of the algorithms created before the Common Era (AD) are still in use today. One such algorithm was first described in Euclid's Elements (~ 300 BC) and has come to be known as the Euclidean Algorithm.
The algorithm is a simple way to find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers, which is useful for a number of different applications (like reducing fractions). The first method (envisioned by Euclid) uses simple subtraction:
function s:euclid_sub(a, b)
let l:a = abs(a:a)
let l:b = abs(a:b)
while l:a != l:b
if l:a > l:b
let l:a -= l:b
else
let l:b -= l:a
endif
endwhile
return l:a
endfunction
int euclid_sub(int a, int b) {
a = abs(a);
b = abs(b);
while (a != b) {
if (a > b) {
a -= b;
} else {
b -= a;
}
}
return a;
}
public int EuclidSub(int a, int b)
{
// Math.Abs for negative number support
a = Math.Abs(a);
b = Math.Abs(b);
while (a != b)
{
if (a > b)
a = a - b;
else
b = b - a;
}
return a;
}
(defn euclid-sub [a b]
(loop [i (Math/abs a) j (Math/abs b)]
(if (= i j)
i
(if (> i j)
(recur (- i j) j)
(recur i (- j i))))))
int euclid_sub(int a, int b) {
a = std::abs(a);
b = std::abs(b);
while (a != b) {
if (a > b) {
a -= b;
} else {
b -= a;
}
}
return a;
}
public static int euclidSub(int a, int b) {
a = Math.abs(a);
b = Math.abs(b);
while (a != b) {
if (a > b) {
a -= b;
} else {
b -= a;
}
}
return a;
}
fun euclidSub(a: Int, b: Int): Int {
var a = a.absoluteValue
var b = b.absoluteValue
while (a != b) {
if (a > b) a -= b
else b -= a
}
return a
}
function euclidSub(a, b) {
a = Math.abs(a);
b = Math.abs(b);
while (a !== b) {
if (a > b) {
a -= b;
} else {
b -= a;
}
}
return a;
}
(defun euclid-sub (a b)
"Finds the greatest common divsor for any two integers"
(defun euclid-sub* (a b)
"Finds the greatest common divisor for any two positive integers"
(if (eql a b)
a
(if (> a b)
(euclid-sub* (- a b) b)
(euclid-sub* a (- b a)))))
(euclid-sub* (abs a) (abs b)))
def euclid_sub(a, b):
a = abs(a)
b = abs(b)
if a == 0:
return b
elif b == 0:
return a
while a != b:
if a > b:
a -= b
else:
b -= a
return a
euclidSub :: Integer -> Integer -> Integer
euclidSub a b = inner (abs a) (abs b)
where
inner x y
-- if a = b, then the gcd is a
| x == y = x
-- if a < b: Recursively call euclidSub with the a and (b-a) as new inputs
| x < y = euclidSub x (y - x)
-- otherwise: Recursively call euclidSub with the a and (b-a) as new inputs
| otherwise = euclidSub (x - y) y
fn euclid_sub(mut a: i64, mut b: i64) -> i64 {
a = a.abs();
b = b.abs();
while a != b {
if a < b {
b -= a;
} else {
a -= b;
}
}
a
}
let euclid_sub a b =
let rec inner a b =
if a = b then
a
else if a < b then
inner a (b - a)
else
inner (a - b) b
in (inner (abs a) (abs b))
func euclidSub(a, b int) int {
a = abs(a)
b = abs(b)
for a != b {
if a > b {
a -= b
} else {
b -= a
}
}
return a
}
func euclidSub(a: Int, b: Int) -> Int {
var a = abs(a)
var b = abs(b)
while (a != b) {
if (a > b) {
a -= b
} else {
b -= a
}
}
return a
}
function gcd = euclidSub(a,b)
a = abs(a);
b = abs(b);
while a ~= b
if a > b
a = a - b;
else
b = b - a;
end
end
gcd = a;
end
local function euclid_sub(a, b)
a = math.abs(a)
b = math.abs(b)
while a ~= b do
if a > b then
a = a-b
else
b = b-a
end
end
return a
end
function euclid_sub(a::Int64, b::Int64)
a = abs(a)
b = abs(b)
while (a != b)
if (a > b)
a -= b
else
b -= a
end
end
return a
end
func euclid_sub(in1, in2: int): int =
var
a = abs(in1)
b = abs(in2)
while a != b:
if a > b:
a -= b
else:
b -= a
result = a
euclid_sub:
mov rax, rdi # Get abs of a
sar rax, 31
xor rdi, rax
sub rdi, rax
mov rax, rsi # Get abs of b
sar rax, 31
xor rsi, rax
sub rsi, rax
jmp check
loop:
cmp rdi, rsi # Find which is bigger
jle if_true
sub rdi, rsi # If a is bigger then a -= b
jmp check
if_true:
sub rsi, rdi # Else b -= a
check:
cmp rsi, rdi # Check if a and b are not equal
jne loop
mov rax, rdi # Return results
INTEGER FUNCTION euclid_sub(a, b)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER, INTENT(INOUT) :: a, b
a = ABS(a)
b = ABS(b)
DO WHILE (a /= b)
IF (a > b) THEN
a = a - b
ELSE
b = b - a
END IF
END DO
euclid_sub = a
END FUNCTION euclid_sub
function euclid_sub(int $a, int $b): int
{
$a = abs($a);
$b = abs($b);
while ($a !== $b) {
if ($a > $b) {
$a = $a - $b;
} else {
$b = $b - $a;
}
}
return $a;
}
: euclid- ( a b -- gcd )
[ abs ] bi@
[ 2dup = ]
[
! make sure the lower number is deeper
2dup >= [ swap ] when
over -
! leaves us with stack { <lower> <greater - lower> }
]
until
! we have the GCD twice now, drop one
drop
;
Euclidian algorithm subtraction method.
Enter two positive integers.
The
end.
def euclid_sub(a: Int, b: Int): Int =
(Math.abs(a), Math.abs(b)) match {
case (0, _) | (_, 0) => 0
case (x, y) if x < y => euclid_sub(x, y - x)
case (x, y) if x > y => euclid_sub(x - y, y)
case _ => a
(define (euclid_sub a b)
(local ((define (euclid_sub* x y)
(if (= x y)
x
(if (> x y)
(euclid_sub* (- x y) y)
(euclid_sub* x (- y x))
)
)
)) (euclid_sub* (abs a) (abs b))
)
)
def gcd_minus(a, b)
a = a.abs
b = b.abs
until a == b
if a > b
a -= b
else
b -= a
end
end
a
end
Integer>>euclidSub: secondNumber
"Euclidean algorithm with subtraction"
| a b |
a := self abs.
b := secondNumber abs.
[ a == b ] whileFalse: [
a > b ifTrue: [
a := a - b.
] ifFalse: [
b := b - a.
].
].
^a.
🐇 ❗️ 🔼 a 🔢 b 🔢 ➡️ 🔢 🍇
💭 Use 🏧 (returns the absolute value) to support negative numbers.
🏧a ❗️ ➡️ 🖍🆕var_a
🏧b ❗️ ➡️ 🖍🆕var_b
️🔁 ❎ var_a 🙌 var_b ❗️ 🍇
↪️ var_a ▶️ var_b 🍇
var_a ⬅️ ➖ var_b
🍉
🙅 🍇
var_b ⬅️ ➖ var_a
🍉
🍉
↩️ var_a
🍉
HOW IZ I UKLIDSUP YR NUM1 AN YR NUM2
NUM1 R I IZ ABZ YR NUM1 MKAY
NUM2 R I IZ ABZ YR NUM2 MKAY
IM IN YR LOOP
BOTH SAEM NUM1 AN NUM2, O RLY?
YA RLY, FOUND YR NUM1
OIC
DIFFRINT NUM1 AN SMALLR OF NUM1 AN NUM2, O RLY?
YA RLY, NUM1 R DIFF OF NUM1 AN NUM2
NO WAI, NUM2 R DIFF OF NUM2 AN NUM1
OIC
IM OUTTA YR LOOP
IF U SAY SO
euclid_sub() {
local a
local b
a=$(abs "$1")
b=$(abs "$2")
while (( a != b )); do
if (( a > b )); then
((a -= b))
else
((b -= a))
fi
done
printf "%s" "$a"
}
// Euclidean algorithm with subtraction
int euclid_sub(int a, int b) {
a = abs(a);
b = abs(b);
while (a != b) {
if (a > b) {
a -= b;
} else {
b -= a;
}
}
return a;
}
(define (euclid-sub a b)
(cond
[(or (negative? a)(negative? b))(euclid-sub (abs a)(abs b))]
[(eq? a b) a]
[(> a b)(euclid-sub(- a b) b)]
[else
(euclid-sub a (- b a))]))
leave one line empty:
function Sub-Euclid($a, $b) {
$a = [Math]::Abs($a)
$b = [Math]::Abs($b)
while ($a -ne $b) {
if ($a -gt $b) {
$a = $a - $b
} else {
$b = $b - $a
}
}
return $a
}
def euclid_sub(int(a), 0) = a
addpattern def euclid_sub(0, int(b)) = b
addpattern def euclid_sub(int(a), int(b)):
if a < b:
return euclid_sub(a, b - a)
elif b < a:
return euclid_sub(a - b, b)
return a
Here, we simply line the two numbers up every step and subtract the lower value from the higher one every timestep. Once the two values are equal, we call that value the greatest common divisor. A graph of a and b as they change every step would look something like this:
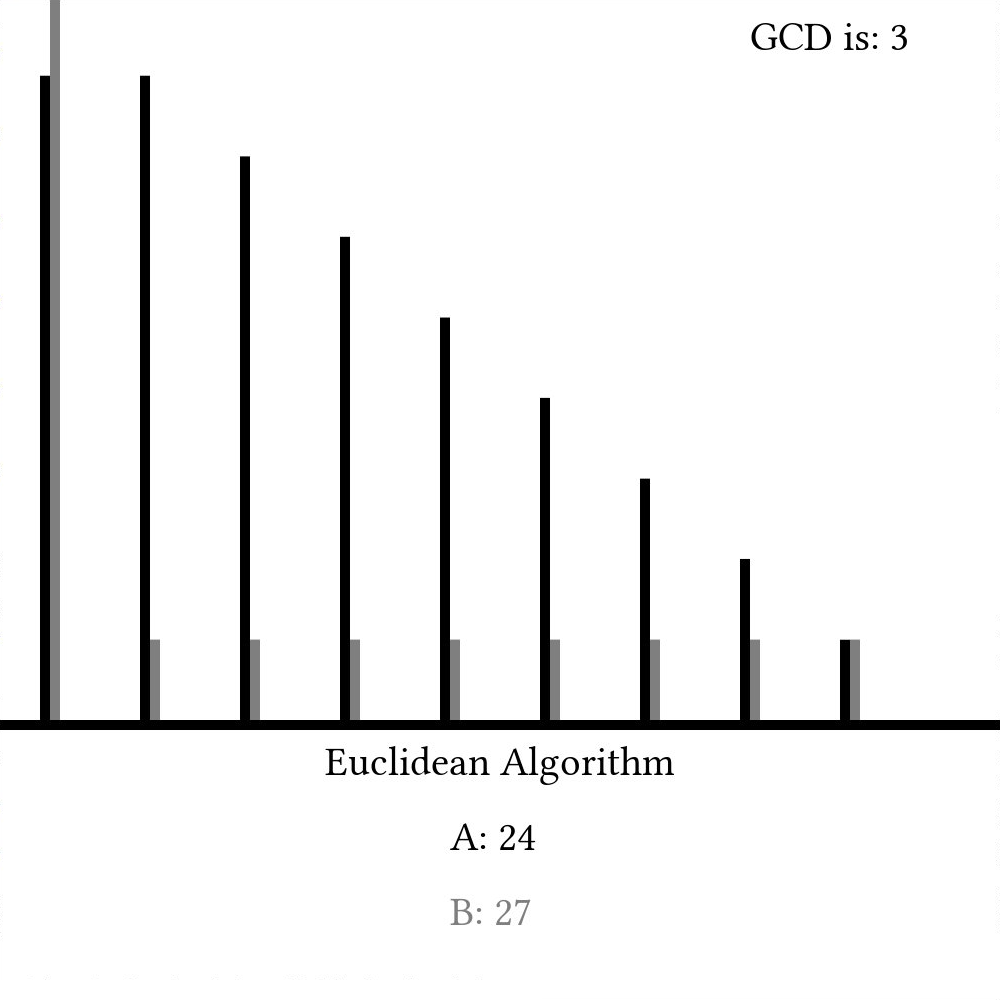
Modern implementations, though, often use the modulus operator (%) like so
function s:euclid_mod(a, b)
let l:a = abs(a:a)
let l:b = abs(a:b)
while l:b != 0
let l:c = l:b
let l:b = l:a % l:b
let l:a = l:c
endwhile
return l:a
endfunction
int euclid_mod(int a, int b) {
a = abs(a);
b = abs(b);
while (b != 0) {
int temp = b;
b = a % b;
a = temp;
}
return a;
}
public int EuclidMod(int a, int b)
{
// Math.Abs for negative number support
a = Math.Abs(a);
b = Math.Abs(b);
while (b != 0)
{
var temp = b;
b = a % b;
a = temp;
}
return a;
}
(defn euclid-mod [a b]
(loop [i (Math/abs a) j (Math/abs b)]
(if (zero? j)
i
(recur j (% i j)))))
// Euclidean algorithm using modulus
int euclid_mod(int a, int b) {
a = std::abs(a);
b = std::abs(b);
while (b != 0) {
a = std::exchange(b, a % b);
}
return a;
}
public static int euclidMod(int a, int b) {
while (b != 0) {
int tmp = b;
b = a % b;
a = tmp;
}
return a;
}
fun euclidMod(a: Int, b: Int): Int {
var a = a.absoluteValue
var b = b.absoluteValue
while (b != 0) {
val tmp = b
b = a % b
a = tmp
}
return a
}
function euclidMod(a, b) {
a = Math.abs(a);
b = Math.abs(b);
let temp;
while (b !== 0) {
temp = b;
b = a % b;
a = temp;
}
return a;
}
(defun euclid-mod (a b)
"Finds the greatest common divisor for any two integers"
(if (zerop b)
(abs a)
(euclid-mod b (mod a b))))
def euclid_mod(a, b):
a = abs(a)
b = abs(b)
while b > 0:
a, b = b, a % b
return a
euclidMod :: Integer -> Integer -> Integer
euclidMod a b = inner (abs a) (abs b)
where
-- if a divides b, then gcd is a
inner x 0 = x
-- otherwise, recursively call inner with b and (a mod b) as new inputs
inner x y = inner y (x `mod` y)
fn euclid_rem(mut a: i64, mut b: i64) -> i64 {
a = a.abs();
b = b.abs();
while b != 0 {
let tmp = b;
b = a % b;
a = tmp;
}
a
}
let euclid_mod a b =
let rec inner a = function
| 0 -> a
| b -> inner b (a mod b)
in (inner (abs a) (abs b))
func euclidMod(a, b int) int {
a = abs(a)
b = abs(b)
for b != 0 {
a, b = b, a%b
}
return a
}
func euclidMod(a: Int, b: Int) -> Int {
var a = abs(a);
var b = abs(b);
while (b != 0) {
let temp = b
b = a % b
a = temp
}
return a
}
function gcd = euclidMod(a,b)
a=abs(a);
b=abs(b);
while b > 0
temp = b;
b = mod(a,b);
a = temp;
end
gcd = a;
end
local function euclid_mod(a, b)
a = math.abs(a)
b = math.abs(b)
while b ~= 0 do
a, b = b, a%b
end
return a
end
function euclid_mod(a::Int64, b::Int64)
a = abs(a)
b = abs(b)
while(b != 0)
b,a = a%b,b
end
return a
end
func euclid_mod(in1, in2: int): int =
var
a = abs(in1)
b = abs(in2)
while b != 0:
let temp: int = b
b = a mod b
a = temp;
result = a
# rdi - a
# rsi - b
# RET rax - gcd of a and b
euclid_mod:
mov rax, rdi # Get abs of a
sar rax, 31
xor rdi, rax
sub rdi, rax
mov rax, rsi # Get abs of b
sar rax, 31
xor rsi, rax
sub rsi, rax
jmp mod_check
mod_loop:
xor rdx, rdx # Take the mod of a and b
mov rax, rdi
div rsi
mov rdi, rsi # Set b to the mod of a and b
mov rsi, rdx # Set a to b
mod_check:
cmp rsi, 0 # Check if b is non-zero
jne mod_loop
mov rax, rdi # Return the result
INTEGER FUNCTION euclid_mod(a, b)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER, INTENT(INOUT) :: a, b
INTEGER :: temp
DO WHILE (b > 0)
temp = b
b = MODULO(a,b)
a = temp
END DO
euclid_mod = a
END FUNCTION euclid_mod
function euclid_mod(int $a, int $b): int
{
$a = abs($a);
$b = abs($b);
while ($b !== 0) {
list($b, $a) = [$a % $b, $b];
}
return $a;
}
: euclid% ( a b -- gcd )
[ abs ] bi@ ! take both absolute values
[ dup zero? ] ! check if `b` (on top) is 0
[
! a b -> a b b -> b a b -> b a%b
dup -rot mod
]
until
! the zero is on top, so get rid of it
drop
;
Euclidian algorithm modulo method.
Enter two positive integers.
The
end.
def euclid_mod(a: Int, b: Int): Int =
(Math.abs(a), Math.abs(b)) match {
case (_, 0) => a
case (a, b) => euclid_mod(b, a % b)
(define (euclid_mod a b)
(local ((define (euclid_mod* a b)
(if (= 0 b)
(abs a)
(euclid_mod* b (modulo a b))
)
)) (euclid_mod* a b)
)
)
def gcd_mod(a, b)
a = a.abs
b = b.abs
a, b = b, a%b until b.zero?
a
end
Integer>>euclidMod: secondNumber
"Euclidean algorithm with modulus."
| a b oldB |
a := self abs.
b := secondNumber abs.
[ b == 0 ] whileFalse: [
oldB := b.
b := a % b.
a := oldB.
].
^a.
🐇 ❗️ ⏫ a 🔢 b 🔢 ➡️ 🔢 🍇
💭 Use 🏧 (returns the absolute value) to support negative numbers.
🏧a ❗️ ➡️ 🖍🆕var_a
🏧b ❗️ ➡️ 🖍🆕var_b
️🔁 ❎ var_b 🙌 0 ❗️ 🍇
var_b ➡️ temp
var_a 🚮 var_b ➡️ 🖍var_b
temp ➡️ 🖍var_a
🍉
↩️ var_a
🍉
HOW IZ I UKLIDMOD YR NUM1 AN YR NUM2
NUM1 R I IZ ABZ YR NUM1 MKAY
NUM2 R I IZ ABZ YR NUM2 MKAY
IM IN YR LOOP
BOTH SAEM NUM2 AN 0, O RLY?
YA RLY, FOUND YR NUM1
OIC
I HAS A TMP ITZ NUM2
NUM2 R MOD OF NUM1 AN NUM2
NUM1 R TMP
IM OUTTA YR LOOP
IF U SAY SO
euclid_mod() {
local a
local b
a=$(abs "$1")
b=$(abs "$2")
while (( b != 0 )); do
((tmp = b))
((b = a % b))
((a = tmp))
done
printf "%s" "$a"
}
// Euclidean algorithm using modulus
int euclid_mod(int a, int b) {
int tmp;
a = abs(a);
b = abs(b);
while (b != 0) {
tmp = a % b;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
return a;
}
(define (euclid-mod a b)
(if (zero? b)
a
(euclid-mod b (modulo a b))))
leave one line empty:
function Mod-Euclid($a, $b) {
$a = [Math]::Abs($a)
$b = [Math]::Abs($b)
while ($b -ne 0) {
$tmp = $b
$b = $a % $b
$a = $tmp
}
return $a
}
def euclid_mod(int(a), 0) = a
addpattern def euclid_mod(0, int(b)) = b
addpattern def euclid_mod(int(a), int(b)) = euclid_mod(b, a % b)
Here, we set b to be the remainder of a%b and a to be whatever b was last timestep. Because of how the modulus operator works, this will provide the same information as the subtraction-based implementation, but when we show a and b as they change with time, we can see that it might take many fewer steps:
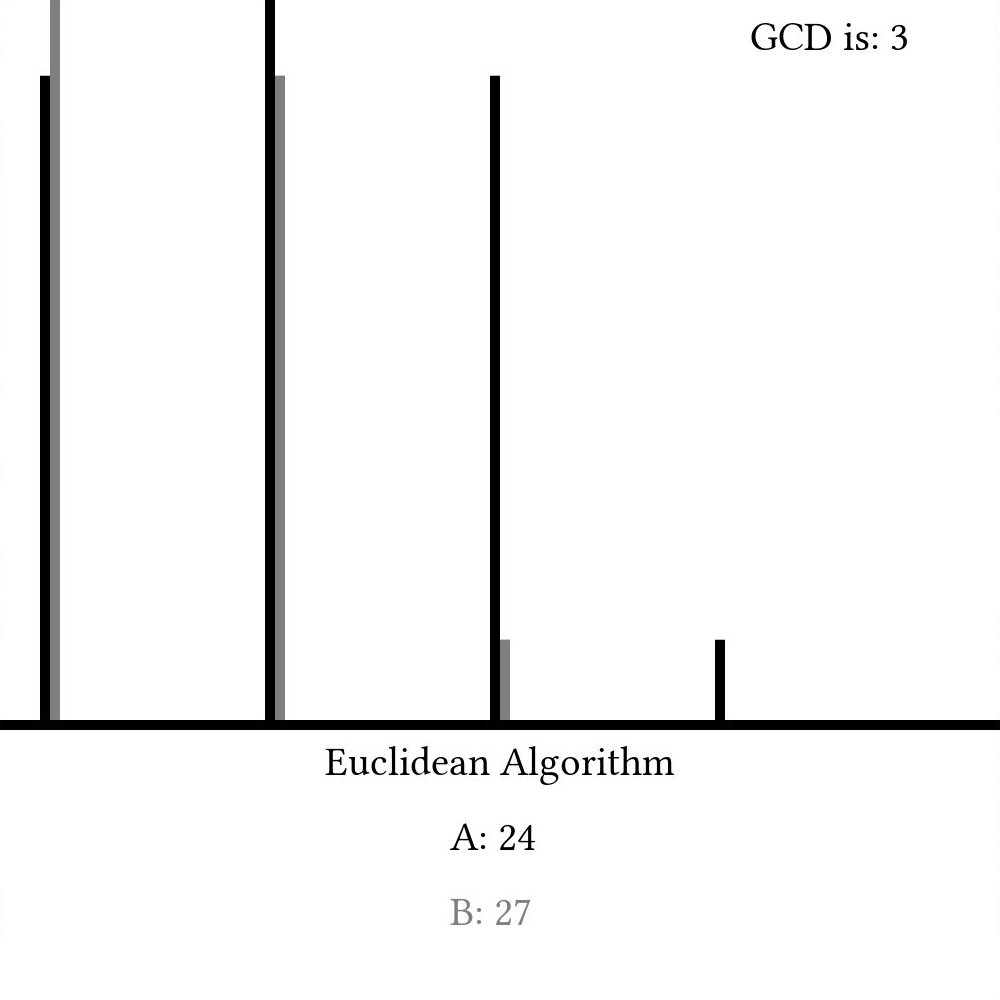
The Euclidean Algorithm is truly fundamental to many other algorithms throughout the history of computer science and will definitely be used again later. At least to me, it's amazing how such an ancient algorithm can still have modern use and appeal. That said, there are still other algorithms out there that can find the greatest common divisor of two numbers that are arguably better in certain cases than the Euclidean algorithm, but the fact that we are discussing Euclid two millennia after his death shows how timeless and universal mathematics truly is. I think that's pretty cool.
Video Explanation
Here's a video on the Euclidean algorithm:
Example Code
function s:euclid_mod(a, b)
let l:a = abs(a:a)
let l:b = abs(a:b)
while l:b != 0
let l:c = l:b
let l:b = l:a % l:b
let l:a = l:c
endwhile
return l:a
endfunction
function s:euclid_sub(a, b)
let l:a = abs(a:a)
let l:b = abs(a:b)
while l:a != l:b
if l:a > l:b
let l:a -= l:b
else
let l:b -= l:a
endif
endwhile
return l:a
endfunction
let s:check_1 = s:euclid_mod(64 * 67, 64 * 71)
let s:check_2 = s:euclid_sub(128 * 12, 128 * 77)
echo 'Modulus-based euclidean algorithm result:' s:check_1
echo 'subtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:' s:check_2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int euclid_mod(int a, int b) {
a = abs(a);
b = abs(b);
while (b != 0) {
int temp = b;
b = a % b;
a = temp;
}
return a;
}
int euclid_sub(int a, int b) {
a = abs(a);
b = abs(b);
while (a != b) {
if (a > b) {
a -= b;
} else {
b -= a;
}
}
return a;
}
int main() {
int check1 = euclid_mod(64 * 67, 64 * 81);
int check2 = euclid_sub(128 * 12, 128 * 77);
printf("[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:\n%d\n", check1);
printf("[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:\n%d\n", check2);
return 0;
}
EuclideanAlgorithm.cs
// submitted by Julian Schacher (jspp)
using System;
namespace EuclideanAlgorithm
{
public class EuclideanAlgorithm
{
public int EuclidSub(int a, int b)
{
// Math.Abs for negative number support
a = Math.Abs(a);
b = Math.Abs(b);
while (a != b)
{
if (a > b)
a = a - b;
else
b = b - a;
}
return a;
}
public int EuclidMod(int a, int b)
{
// Math.Abs for negative number support
a = Math.Abs(a);
b = Math.Abs(b);
while (b != 0)
{
var temp = b;
b = a % b;
a = temp;
}
return a;
}
}
}
Program.cs
// submitted by Julian Schacher (jspp)
using System;
namespace EuclideanAlgorithm
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var euclideanAlgorithm = new EuclideanAlgorithm();
int check = euclideanAlgorithm.EuclidMod(64 * 67, 64 * 81);
int check2 = euclideanAlgorithm.EuclidSub(128 * 12, 128 * 77);
Console.WriteLine("[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:");
Console.WriteLine(check);
Console.WriteLine("[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:");
Console.WriteLine(check2);
}
}
}
;; earthfail
(defn euclid-sub [a b]
(loop [i (Math/abs a) j (Math/abs b)]
(if (= i j)
i
(if (> i j)
(recur (- i j) j)
(recur i (- j i))))))
(defn euclid-mod [a b]
(loop [i (Math/abs a) j (Math/abs b)]
(if (zero? j)
i
(recur j (% i j)))))
(print
(euclid-sub (* 64 67)
(* 64 81))
(euclid-mod (* 128 12)
(* 128 77)))
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
// Euclidean algorithm using modulus
int euclid_mod(int a, int b) {
a = std::abs(a);
b = std::abs(b);
while (b != 0) {
a = std::exchange(b, a % b);
}
return a;
}
// Euclidean algorithm with subtraction
int euclid_sub(int a, int b) {
a = std::abs(a);
b = std::abs(b);
while (a != b) {
if (a > b) {
a -= b;
} else {
b -= a;
}
}
return a;
}
int main() {
auto check1 = euclid_mod(64 * 67, 64 * 81);
auto check2 = euclid_sub(128 * 12, 128 * 77);
std::cout << "[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:\n" << check1 << '\n';
std::cout << "[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:\n" << check2 << '\n';
}
// submitted by lolatomroflsinnlos, modified by xam4lor
public class EuclideanAlgo {
public static int euclidSub(int a, int b) {
a = Math.abs(a);
b = Math.abs(b);
while (a != b) {
if (a > b) {
a -= b;
} else {
b -= a;
}
}
return a;
}
public static int euclidMod(int a, int b) {
while (b != 0) {
int tmp = b;
b = a % b;
a = tmp;
}
return a;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:");
System.out.println(euclidMod(64 * 67, 64 * 81));
System.out.println("[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:");
System.out.println(euclidSub(128 * 12, 128 * 77));
}
}
import kotlin.math.absoluteValue
fun euclidSub(a: Int, b: Int): Int {
var a = a.absoluteValue
var b = b.absoluteValue
while (a != b) {
if (a > b) a -= b
else b -= a
}
return a
}
fun euclidMod(a: Int, b: Int): Int {
var a = a.absoluteValue
var b = b.absoluteValue
while (b != 0) {
val tmp = b
b = a % b
a = tmp
}
return a
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
println("[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:")
println(euclidMod(64 * 67, 64 * 81))
println("[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:")
println(euclidSub(128 * 12, 128 * 77))
}
function euclidMod(a, b) {
a = Math.abs(a);
b = Math.abs(b);
let temp;
while (b !== 0) {
temp = b;
b = a % b;
a = temp;
}
return a;
}
function euclidSub(a, b) {
a = Math.abs(a);
b = Math.abs(b);
while (a !== b) {
if (a > b) {
a -= b;
} else {
b -= a;
}
}
return a;
}
console.log('[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:')
console.log(euclidMod(64 * 67, 64 * 81));
console.log('[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:')
console.log(euclidSub(128 * 12, 128 * 77));
;;;; Euclidean algorithm implementation in Common Lisp
(defun euclid-sub (a b)
"Finds the greatest common divsor for any two integers"
(defun euclid-sub* (a b)
"Finds the greatest common divisor for any two positive integers"
(if (eql a b)
a
(if (> a b)
(euclid-sub* (- a b) b)
(euclid-sub* a (- b a)))))
(euclid-sub* (abs a) (abs b)))
(defun euclid-mod (a b)
"Finds the greatest common divisor for any two integers"
(if (zerop b)
(abs a)
(euclid-mod b (mod a b))))
(format T "[#]~%Modulus-based euclidean algorithm result:~%")
(format T "~d~%" (euclid-sub (* 64 67) (* 64 81)))
(format T "[#]~%Subtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:~%")
(format T "~d~%" (euclid-mod (* 128 12) (* 128 77)))
;; Quick test
(assert
(eql (euclid-sub (* 64 67) (* 64 81))
(gcd (* 64 67) (* 64 81))))
(assert
(eql (euclid-mod (* 64 67) (* 64 81))
(gcd (* 64 67) (* 64 81))))
def euclid_mod(a, b):
a = abs(a)
b = abs(b)
while b > 0:
a, b = b, a % b
return a
def euclid_sub(a, b):
a = abs(a)
b = abs(b)
if a == 0:
return b
elif b == 0:
return a
while a != b:
if a > b:
a -= b
else:
b -= a
return a
if __name__=="__main__":
print('[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:'),
print(euclid_mod(64 * 67, 64 * 81))
print('[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:')
print(euclid_sub(128 * 12, 128 * 77))
-- Method 1: Euclid's original subtraction algorithm
euclidSub :: Integer -> Integer -> Integer
euclidSub a b = inner (abs a) (abs b)
where
inner x y
-- if a = b, then the gcd is a
| x == y = x
-- if a < b: Recursively call euclidSub with the a and (b-a) as new inputs
| x < y = euclidSub x (y - x)
-- otherwise: Recursively call euclidSub with the a and (b-a) as new inputs
| otherwise = euclidSub (x - y) y
-- _______________________________________________________________________
-- Method 2: Modern implemetation - The modulus method.
euclidMod :: Integer -> Integer -> Integer
euclidMod a b = inner (abs a) (abs b)
where
-- if a divides b, then gcd is a
inner x 0 = x
-- otherwise, recursively call inner with b and (a mod b) as new inputs
inner x y = inner y (x `mod` y)
-- _________________________________________________________________________
-- Examples
main :: IO ()
main = do
let chk1 = euclidMod (64 * 67) (64 * 81)
chk2 = euclidSub (128 * 12) (128 * 77)
putStrLn "[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:"
print chk1
putStrLn "[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:"
print chk2
// contributed by Nicole Mazzuca (ubsan)
fn euclid_sub(mut a: i64, mut b: i64) -> i64 {
a = a.abs();
b = b.abs();
while a != b {
if a < b {
b -= a;
} else {
a -= b;
}
}
a
}
fn euclid_rem(mut a: i64, mut b: i64) -> i64 {
a = a.abs();
b = b.abs();
while b != 0 {
let tmp = b;
b = a % b;
a = tmp;
}
a
}
fn main() {
let chk1 = euclid_rem(64 * 67, 64 * 81);
let chk2 = euclid_sub(128 * 12, 128 * 77);
println!("[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:\n{}", chk1);
println!("[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:\n{}", chk2);
}
(* contributed by Nicole Mazzuca (ubsan) *)
let euclid_mod a b =
let rec inner a = function
| 0 -> a
| b -> inner b (a mod b)
in (inner (abs a) (abs b))
let euclid_sub a b =
let rec inner a b =
if a = b then
a
else if a < b then
inner a (b - a)
else
inner (a - b) b
in (inner (abs a) (abs b))
let chk1 = euclid_mod (64 * 67) (64 * 81)
let chk2 = euclid_sub (128 * 12) (128 * 77)
let () =
Printf.printf "[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:\n";
chk1 |> print_int |> print_newline;
Printf.printf "[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:\n";
chk2 |> print_int |> print_newline
// Submitted by Chinmaya Mahesh (chin123)
package main
import "fmt"
func abs(a int) int {
if a < 0 {
a = -a
}
return a
}
func euclidMod(a, b int) int {
a = abs(a)
b = abs(b)
for b != 0 {
a, b = b, a%b
}
return a
}
func euclidSub(a, b int) int {
a = abs(a)
b = abs(b)
for a != b {
if a > b {
a -= b
} else {
b -= a
}
}
return a
}
func main() {
check1 := euclidMod(64*67, 64*81)
check2 := euclidSub(128*12, 128*77)
fmt.Println("[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:")
fmt.Println(check1)
fmt.Println("[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:")
fmt.Println(check2)
}
func euclidSub(a: Int, b: Int) -> Int {
var a = abs(a)
var b = abs(b)
while (a != b) {
if (a > b) {
a -= b
} else {
b -= a
}
}
return a
}
func euclidMod(a: Int, b: Int) -> Int {
var a = abs(a);
var b = abs(b);
while (b != 0) {
let temp = b
b = a % b
a = temp
}
return a
}
func main() {
print("[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:")
print(euclidMod(a: 64 * 67, b: 64 * 81))
print("[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:")
print(euclidSub(a: 128 * 12, b: 128 * 77))
}
main()
// Submitted by Max Weinstein
function gcd = euclidSub(a,b)
a = abs(a);
b = abs(b);
while a ~= b
if a > b
a = a - b;
else
b = b - a;
end
end
gcd = a;
end
function gcd = euclidMod(a,b)
a=abs(a);
b=abs(b);
while b > 0
temp = b;
b = mod(a,b);
a = temp;
end
gcd = a;
end
function euclid()
['[#] Modulus-based euclidean algorithm result: ',num2str(euclidMod(64 * 67, 64 * 81))]
['[#] Subtraction-based euclidean algorithm result: ',num2str(euclidSub(128 * 12, 128 * 77))]
end
local function euclid_sub(a, b)
a = math.abs(a)
b = math.abs(b)
while a ~= b do
if a > b then
a = a-b
else
b = b-a
end
end
return a
end
local function euclid_mod(a, b)
a = math.abs(a)
b = math.abs(b)
while b ~= 0 do
a, b = b, a%b
end
return a
end
local function main()
print("[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:")
print(euclid_mod(64 * 67, 64 * 81))
print("[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:")
print(euclid_sub(128 * 12, 128 * 77))
end
main()
function euclid_mod(a::Int64, b::Int64)
a = abs(a)
b = abs(b)
while(b != 0)
b,a = a%b,b
end
return a
end
function euclid_sub(a::Int64, b::Int64)
a = abs(a)
b = abs(b)
while (a != b)
if (a > b)
a -= b
else
b -= a
end
end
return a
end
function main()
check1 = euclid_mod(64 * 67, 64 * 81);
check2 = euclid_sub(128 * 12, 128 * 77);
println("[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:\n$(check1)")
println("[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:\n$(check2)")
end
main()
func euclid_mod(in1, in2: int): int =
var
a = abs(in1)
b = abs(in2)
while b != 0:
let temp: int = b
b = a mod b
a = temp;
result = a
func euclid_sub(in1, in2: int): int =
var
a = abs(in1)
b = abs(in2)
while a != b:
if a > b:
a -= b
else:
b -= a
result = a
when isMainModule:
echo "[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:"
echo euclid_sub(64 * 67, 64 * 81)
echo "[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:"
echo euclid_mod(128 * 12, 128 * 77)
.intel_syntax noprefix
.section .rodata
euclid_mod_fmt: .string "[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:\n%d\n"
euclid_sub_fmt: .string "[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:\n%d\n"
.section .text
.global main
.extern printf
# rdi - a
# rsi - b
# RET rax - gcd of a and b
euclid_mod:
mov rax, rdi # Get abs of a
sar rax, 31
xor rdi, rax
sub rdi, rax
mov rax, rsi # Get abs of b
sar rax, 31
xor rsi, rax
sub rsi, rax
jmp mod_check
mod_loop:
xor rdx, rdx # Take the mod of a and b
mov rax, rdi
div rsi
mov rdi, rsi # Set b to the mod of a and b
mov rsi, rdx # Set a to b
mod_check:
cmp rsi, 0 # Check if b is non-zero
jne mod_loop
mov rax, rdi # Return the result
ret
euclid_sub:
mov rax, rdi # Get abs of a
sar rax, 31
xor rdi, rax
sub rdi, rax
mov rax, rsi # Get abs of b
sar rax, 31
xor rsi, rax
sub rsi, rax
jmp check
loop:
cmp rdi, rsi # Find which is bigger
jle if_true
sub rdi, rsi # If a is bigger then a -= b
jmp check
if_true:
sub rsi, rdi # Else b -= a
check:
cmp rsi, rdi # Check if a and b are not equal
jne loop
mov rax, rdi # Return results
ret
main:
mov rdi, 4288 # Call euclid_mod
mov rsi, 5184
call euclid_mod
mov rdi, OFFSET euclid_mod_fmt # Print output
mov rsi, rax
xor rax, rax
call printf
mov rdi, 1536 # Call euclid_sub
mov rsi, 9856
call euclid_sub
mov rdi, OFFSET euclid_sub_fmt # Print output
mov rsi, rax
xor rax, rax
call printf
xor rax, rax # Return 0
ret
INTEGER FUNCTION euclid_sub(a, b)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER, INTENT(INOUT) :: a, b
a = ABS(a)
b = ABS(b)
DO WHILE (a /= b)
IF (a > b) THEN
a = a - b
ELSE
b = b - a
END IF
END DO
euclid_sub = a
END FUNCTION euclid_sub
INTEGER FUNCTION euclid_mod(a, b)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER, INTENT(INOUT) :: a, b
INTEGER :: temp
DO WHILE (b > 0)
temp = b
b = MODULO(a,b)
a = temp
END DO
euclid_mod = a
END FUNCTION euclid_mod
PROGRAM euclidean
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER :: a, b, euclid_sub, euclid_mod
a = 64 * 67
b = 64 * 81
WRITE(*,'(a)') '[#]'
WRITE(*,'(a)') 'Modulus-based euclidean algorithm result:'
WRITE(*, '(g0)') euclid_mod(a, b)
a = 128 * 12
b = 128 * 77
WRITE(*,'(a)') '[#]'
WRITE(*,'(a)') 'Subtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:'
WRITE(*, '(g0)') euclid_sub(a, b)
END PROGRAM euclidean
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
function euclid_sub(int $a, int $b): int
{
$a = abs($a);
$b = abs($b);
while ($a !== $b) {
if ($a > $b) {
$a = $a - $b;
} else {
$b = $b - $a;
}
}
return $a;
}
function euclid_mod(int $a, int $b): int
{
$a = abs($a);
$b = abs($b);
while ($b !== 0) {
list($b, $a) = [$a % $b, $b];
}
return $a;
}
printf('[#]'.PHP_EOL.'Modulus-based euclidean algorithm result:'.PHP_EOL.'%s', euclid_mod(64 * 67, 64 * 81));
echo PHP_EOL;
printf('[#]'.PHP_EOL.'Subtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:'.PHP_EOL.'%s', euclid_sub(128 * 12, 128 * 77));
echo PHP_EOL;
: euclid- ( a b -- gcd )
[ abs ] bi@
[ 2dup = ]
[
! make sure the lower number is deeper
2dup >= [ swap ] when
over -
! leaves us with stack { <lower> <greater - lower> }
]
until
! we have the GCD twice now, drop one
drop
;
: euclid% ( a b -- gcd )
[ abs ] bi@ ! take both absolute values
[ dup zero? ] ! check if `b` (on top) is 0
[
! a b -> a b b -> b a b -> b a%b
dup -rot mod
]
until
! the zero is on top, so get rid of it
drop
;
42 56 euclid% . ! 14
48 180 euclid% . ! 12
42 56 euclid- . ! 14
48 180 euclid- . ! 12
Here is a readable version of the algorithms with comments. First, subtraction method:
Reading the input: a, b
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][LF] push 0
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][TAB][LF] push 1
[TAB][LF][TAB][TAB] readi
[TAB][LF][TAB][TAB] readi
Loop: a, b => a, b-a
[LF][SPACE][SPACE][LF] label_0:
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][LF] push 0
[TAB][TAB][TAB] retrieve
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][TAB][LF] push 1
[TAB][TAB][TAB] retrieve
[TAB][SPACE][SPACE][TAB] sub
[SPACE][LF][SPACE] dup
[LF][TAB][SPACE][TAB][LF] jmp zero label_1
[SPACE][LF][SPACE] dup
[LF][TAB][TAB][TAB][SPACE][LF] jmp neg label_2
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][LF] push 0
[SPACE][LF][TAB] swap
[TAB][TAB][SPACE] store
[LF][SPACE][LF][LF] jmp label_0
Exit when a=b
[LF][SPACE][SPACE][TAB][LF] label_1:
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][LF] push 0
[TAB][TAB][TAB] retrieve
[TAB][LF][SPACE][TAB] printi
[LF][LF][LF] end
If a>b: a, b => a-b, b
[LF][SPACE][SPACE][TAB][SPACE][LF] label_2:
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][LF] push 0
[SPACE][LF][TAB] swap
[TAB][SPACE][SPACE][TAB] sub
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][TAB][LF] push 1
[SPACE][LF][TAB] swap
[TAB][TAB][SPACE] store
[LF][SPACE][LF][LF] jmp label_0
and modulo method:
Reading the input: a, b
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][LF] push 0
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][TAB][LF] push 1
[TAB][LF][TAB][TAB] readi
[TAB][LF][TAB][TAB] readi
Loop: a, b => b, a%b
[LF][SPACE][SPACE][LF] label_0:
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][LF] push 0
[TAB][TAB][TAB] retrieve
[SPACE][LF][SPACE] dup
[LF][TAB][SPACE][TAB][LF] jmp zero label_1
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][TAB][LF] push 1
[TAB][TAB][TAB] retrieve
[SPACE][LF][TAB] swap
[TAB][SPACE][TAB][TAB] mod
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][LF] push 0
[TAB][TAB][TAB] retrieve
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][TAB][LF] push 1
[SPACE][LF][TAB] swap
[TAB][TAB][SPACE] store
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][LF] push 0
[SPACE][LF][TAB] swap
[TAB][TAB][SPACE] store
[LF][SPACE][LF][LF] jmp label_0
Exit when b=0
[LF][SPACE][SPACE][TAB][LF] label_1:
[SPACE][SPACE][SPACE][TAB][LF] push 1
[TAB][TAB][TAB] retrieve
[TAB][LF][SPACE][TAB] printi
[LF][LF][LF][LF] end
object Euclid {
def euclid_sub(a: Int, b: Int): Int =
(Math.abs(a), Math.abs(b)) match {
case (0, _) | (_, 0) => 0
case (x, y) if x < y => euclid_sub(x, y - x)
case (x, y) if x > y => euclid_sub(x - y, y)
case _ => a
}
def euclid_mod(a: Int, b: Int): Int =
(Math.abs(a), Math.abs(b)) match {
case (_, 0) => a
case (a, b) => euclid_mod(b, a % b)
}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
println("[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:")
println(euclid_mod(64 * 67, 64 * 81))
println("[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:")
println(euclid_sub(128 * 12, 128 * 77))
}
}
#lang racket
(define (euclid_sub a b)
(local ((define (euclid_sub* x y)
(if (= x y)
x
(if (> x y)
(euclid_sub* (- x y) y)
(euclid_sub* x (- y x))
)
)
)) (euclid_sub* (abs a) (abs b))
)
)
(define (euclid_mod a b)
(local ((define (euclid_mod* a b)
(if (= 0 b)
(abs a)
(euclid_mod* b (modulo a b))
)
)) (euclid_mod* a b)
)
)
(displayln "[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:")
(displayln (euclid_sub (* 64 67) (* 64 81)))
(displayln "[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:")
(displayln (euclid_mod (* 128 12) (* 128 77)))
def gcd_mod(a, b)
a = a.abs
b = b.abs
a, b = b, a%b until b.zero?
a
end
def gcd_minus(a, b)
a = a.abs
b = b.abs
until a == b
if a > b
a -= b
else
b -= a
end
end
a
end
print "[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:\n"
p gcd_mod(64 * 67, 64 * 81)
print "[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:\n"
p gcd_minus(128 * 12, 128 * 77)
Integer>>euclidSub: secondNumber
"Euclidean algorithm with subtraction"
| a b |
a := self abs.
b := secondNumber abs.
[ a == b ] whileFalse: [
a > b ifTrue: [
a := a - b.
] ifFalse: [
b := b - a.
].
].
^a.
Integer>>euclidMod: secondNumber
"Euclidean algorithm with modulus."
| a b oldB |
a := self abs.
b := secondNumber abs.
[ b == 0 ] whileFalse: [
oldB := b.
b := a % b.
a := oldB.
].
^a.
Transcript show: ((64 * 67) euclidSub: (64 * 81)).
Transcript cr.
Transcript show: ((128 * 12) euclidMod: (128 * 77)).
🐇 ⬆️ 🍇
🐇 ❗️ 🔼 a 🔢 b 🔢 ➡️ 🔢 🍇
💭 Use 🏧 (returns the absolute value) to support negative numbers.
🏧a ❗️ ➡️ 🖍🆕var_a
🏧b ❗️ ➡️ 🖍🆕var_b
️🔁 ❎ var_a 🙌 var_b ❗️ 🍇
↪️ var_a ▶️ var_b 🍇
var_a ⬅️ ➖ var_b
🍉
🙅 🍇
var_b ⬅️ ➖ var_a
🍉
🍉
↩️ var_a
🍉
🐇 ❗️ ⏫ a 🔢 b 🔢 ➡️ 🔢 🍇
💭 Use 🏧 (returns the absolute value) to support negative numbers.
🏧a ❗️ ➡️ 🖍🆕var_a
🏧b ❗️ ➡️ 🖍🆕var_b
️🔁 ❎ var_b 🙌 0 ❗️ 🍇
var_b ➡️ temp
var_a 🚮 var_b ➡️ 🖍var_b
temp ➡️ 🖍var_a
🍉
↩️ var_a
🍉
🍉
🏁 🍇
😀 🔡 ️🔼🐇⬆️ 🤜64 ✖️ 67🤛 🤜64 ✖️ 81🤛 ❗️ 10 ❗️❗️
😀 🔡 ️⏫🐇⬆️ 🤜128 ✖️ 12🤛 🤜128 ✖️ 77🤛 ❗️ 10 ❗️❗️
🍉
HAI 1.2
HOW IZ I ABZ YR NUM
DIFFRINT NUM AN BIGGR OF NUM AN 0, O RLY?
YA RLY, FOUND YR DIFF OF 0 AN NUM
NO WAI, FOUND YR NUM
OIC
IF U SAY SO
HOW IZ I UKLIDMOD YR NUM1 AN YR NUM2
NUM1 R I IZ ABZ YR NUM1 MKAY
NUM2 R I IZ ABZ YR NUM2 MKAY
IM IN YR LOOP
BOTH SAEM NUM2 AN 0, O RLY?
YA RLY, FOUND YR NUM1
OIC
I HAS A TMP ITZ NUM2
NUM2 R MOD OF NUM1 AN NUM2
NUM1 R TMP
IM OUTTA YR LOOP
IF U SAY SO
HOW IZ I UKLIDSUP YR NUM1 AN YR NUM2
NUM1 R I IZ ABZ YR NUM1 MKAY
NUM2 R I IZ ABZ YR NUM2 MKAY
IM IN YR LOOP
BOTH SAEM NUM1 AN NUM2, O RLY?
YA RLY, FOUND YR NUM1
OIC
DIFFRINT NUM1 AN SMALLR OF NUM1 AN NUM2, O RLY?
YA RLY, NUM1 R DIFF OF NUM1 AN NUM2
NO WAI, NUM2 R DIFF OF NUM2 AN NUM1
OIC
IM OUTTA YR LOOP
IF U SAY SO
I HAS A CHECK1 ITZ I IZ UKLIDMOD YR PRODUKT OF 64 AN 67 AN YR PRODUKT OF 64 AN 81 MKAY
I HAS A CHECK2 ITZ I IZ UKLIDSUP YR PRODUKT OF 128 AN 12 AN YR PRODUKT OF 128 AN 77 MKAY
VISIBLE CHECK1
VISIBLE CHECK2
KTHXBYE
#!/usr/bin/env bash
abs() {
local ret=$1
if (( ret < 0 )); then
((ret *= -1))
fi
printf "%s" "$ret"
}
euclid_mod() {
local a
local b
a=$(abs "$1")
b=$(abs "$2")
while (( b != 0 )); do
((tmp = b))
((b = a % b))
((a = tmp))
done
printf "%s" "$a"
}
euclid_sub() {
local a
local b
a=$(abs "$1")
b=$(abs "$2")
while (( a != b )); do
if (( a > b )); then
((a -= b))
else
((b -= a))
fi
done
printf "%s" "$a"
}
result=$(euclid_mod $((64 * 67)) $((64 * 81)))
echo -e "[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:\n$result"
result=$(euclid_sub $((128 * 12)) $((128 * 77)))
echo -e "[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:\n$result"
import std.stdio;
import std.math;
// Euclidean algorithm using modulus
int euclid_mod(int a, int b) {
int tmp;
a = abs(a);
b = abs(b);
while (b != 0) {
tmp = a % b;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
return a;
}
// Euclidean algorithm with subtraction
int euclid_sub(int a, int b) {
a = abs(a);
b = abs(b);
while (a != b) {
if (a > b) {
a -= b;
} else {
b -= a;
}
}
return a;
}
void main()
{
auto check1 = euclid_mod(64 * 67, 64 * 81);
auto check2 = euclid_sub(128 * 12, 128 * 77);
writeln("[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:\n", check1);
writeln("[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:\n", check2);
}
A text version of the program is provided for both versions.
Subtraction
COMMAND STATE OF STACK
in(number) A // Take A as an input
duplicate AA // Start to take the absolute value of A
push 1 1AA
duplicate 11AA
subtract 0AA
greater 0/1A // 1 if A > 0, 0 if A <= 0
not 1/0A // 0 if A > 0, 1 if A <= 0
push 1 1 1/0 A
push 3 31 1/0 A
subtract -2 1/0 A
multiply -2/0 A
push 1 1 -2/0 A
add -1/1 A
multiply A // A should now be an absolute value
in(number) BA // Take B as an input
duplicate BBA // Start to take the absolute value of B
push 1 1BBA
duplicate 11BBA
subtract 0BBA
greater 0/1BA // 1 if B > 0, 0 if B <= 0
not 1/0BA // 0 if B > 0, 1 if B <= 0
push 1 1 1/0 BA
push 3 31 1/0 BA
subtract -2 1/0 BA
multiply -2/0 BA
push 1 1 -2/0 BA
add -1/1 BA
multiply BA // B should now be an absolute value
// Start of the main loop while a ≠ b
duplicate BBA
push 3 3BBA
push 2 23BBA
roll ABB
duplicate AABB
push 4 4AABB
push 1 14AABB
roll ABBA
subtract 0/x BA
not 1/0 BA // 1 if a = b and 0 if a ≠ b
not 0/1 BA // 1 if a ≠ b and 0 if a = b
pointer BA // If a ≠ b, the DP should change one clockwise, otherwise, go straight ahead.
// Go left if a ≠ b (DP changed one clockwise)
duplicate BBA
push 3 3BBA
push 2 23BBA
roll ABB
duplicate AABB
push 4 4AABB
push 1 14AABB
roll ABBA
push 2 2ABBA
push 1 12ABBA
roll BABA
greater 0/1 BA // A > B; 1 if true; 0 if false
pointer BA // If A > B, DP goes one clockwise, otherwise, DP stays the same.
// If A > B (DP has changed 1 clockwise)
duplicate BBA
push 3 3BBA
push 1 13BBA
roll BAB
subtract AB // A = A - B
push 2 2AB
push 1 12AB
roll BA
// Go back to start of loop
// If B > A (DP stayed the same)
push 2 2BA
push 1 12BA
roll AB
duplicate AAB
push 3 3AAB
push 1 13AAB
roll ABA
subtract BA // B = B - A
// Go back to start of loop
// Go down if a = b (end of while loop)
pop A
out(number) - // Print out A when done.
Modulo
COMMAND STATE OF STACK
in(number) A
in(number) BA
// Start of loop
duplicate BBA
not 0/1 BA
not 1/0 BA
pointer BA
// Go down if b ≠ 0
duplicate TBA
push 3 3TBA
push 1 13TBA
roll BAT
mod BA // b = a mod b; a = t
// Go back to the start of the loop
// Go right if b = 0
pop A
out(number) - // Print out A when done.
(define (euclid-sub a b)
(cond
[(or (negative? a)(negative? b))(euclid-sub (abs a)(abs b))]
[(eq? a b) a]
[(> a b)(euclid-sub(- a b) b)]
[else
(euclid-sub a (- b a))]))
(define (euclid-mod a b)
(if (zero? b)
a
(euclid-mod b (modulo a b))))
(display "[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:") (newline)
(display (euclid-mod (* 64 67) (* 64 81))) (newline)
(display "[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:") (newline)
(display (euclid-sub (* 128 12) (* 128 77))) (newline)
function Sub-Euclid($a, $b) {
$a = [Math]::Abs($a)
$b = [Math]::Abs($b)
while ($a -ne $b) {
if ($a -gt $b) {
$a = $a - $b
} else {
$b = $b - $a
}
}
return $a
}
function Mod-Euclid($a, $b) {
$a = [Math]::Abs($a)
$b = [Math]::Abs($b)
while ($b -ne 0) {
$tmp = $b
$b = $a % $b
$a = $tmp
}
return $a
}
Write-Host "[#]`nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:`n$(Mod-Euclid $(64 * 67) $(64 * 81))"
Write-Host "[#]`nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:`n$(Sub-Euclid $(128 * 12) $(128 * 77))"
def euclid_sub(int(a), 0) = a
addpattern def euclid_sub(0, int(b)) = b
addpattern def euclid_sub(int(a), int(b)):
if a < b:
return euclid_sub(a, b - a)
elif b < a:
return euclid_sub(a - b, b)
return a
def euclid_mod(int(a), 0) = a
addpattern def euclid_mod(0, int(b)) = b
addpattern def euclid_mod(int(a), int(b)) = euclid_mod(b, a % b)
if __name__ == '__main__':
print('[#]\nModulus-based euclidean algorithm result:')
print(euclid_mod(64 * 67, 64 * 81))
print('[#]\nSubtraction-based euclidean algorithm result:')
print(euclid_sub(128 * 12, 128 * 77))
License
Code Examples
The code examples are licensed under the MIT license (found in LICENSE.md).
Text
The text of this chapter was written by James Schloss and is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Images/Graphics
- The image "Euclidsub" was created by James Schloss and is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The image "Euclidmod" was created by James Schloss and is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Pull Requests
After initial licensing (#560), the following pull requests have modified the text or graphics of this chapter:
- none



