Tree Traversal
Trees are naturally recursive data structures, and because of this, we cannot access their elements like we might access the elements of a vector or array. Instead, we need to use more interesting methods to work through each element. This is often called Tree Traversal, and there are many different ways to do this. For now, we will restrict the discussion to two common and related methods of tree traversal: Depth-First and Breadth-First Search. Note that trees vary greatly in shape and size depending on how they are used; however, they are composed primarily of nodes that house other, children nodes, like so:
struct Node
children::Vector{Node}
ID::Int64
Node(ID::Int64) = new(Vector{Node}(), ID)
end
struct node {
std::vector<node> children;
size_t value;
};
public class Tree
{
public int Id { get; private set; }
private List<Tree> _children = new List<Tree>();
struct node {
struct node *children;
size_t children_size;
int id;
};
private class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
public ArrayList<Node> children;
public int id;
public Node(int id) {
this.children = new ArrayList<Node>();
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node other) {
// Need to implement Comparable<Node> and override this
// method because of the method BFSQueue() which uses Queues
// and must know how to check if two nodes are the same or not
return Integer.compare(this.id, other.id);
}
}
function createTree(rows, children) {
if (rows === 0) {
return { id: rows, children: [] };
}
return {
id: rows,
children: [...Array(children).keys()].map(() => createTree(rows - 1, children))
};
}
As a note, a node struct is not necessary in javascript, so this is an example of how a tree might be constructed.
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.data = None
self.children = []
struct Node {
children: Vec<Node>,
value: u64,
}
data Tree a = Node
{ node :: a,
forest :: [Tree a]
}
class Node {
var value: Int
var children: [Node]?
init(value: Int, children: [Node]) {
self.value = value
self.children = children
}
}
class Tree implements JsonSerializable
{
private $id;
private $children = [];
public function __construct(int $id, array $children = [])
{
$this->id = $id;
$this->children = $children;
}
public function getId(): int
{
return $this->id;
}
public function getChildren(): array
{
return $this->children;
}
public function addChild(Tree $child): void
{
$this->children[] = $child;
}
public function jsonSerialize(): array
{
return [
'id' => $this->id,
'children' => $this->children,
];
}
}
class Node
property id, children
def initialize(@id : Int32, @children : Array(Node))
end
end
Object subclass: #Node
instanceVariableNames: 'children data'
classVariableNames: ''
package: ''
Node>>children
"Children getter."
^ children
Node>>children: newChildren
"Children setter."
children := newChildren.
Node>>data
"Data getter"
^ data
Node>>data: newData
"Data setter"
data := newData.
type node struct {
id int
children []*node
}
.equ tree_children, 0
.equ tree_num_children, 8
.equ tree_value, 12
.equ tree_size, 16
🦃 ⏹ 🍇
🔘 ⏫
(defstruct node data children)
node = @(k,v) containers.Map(k,v);
data Node(value: int, children: Node[])
Because of this, the most straightforward way to traverse the tree might be recursive. This naturally leads us to the Depth-First Search (DFS) method:
function DFS_recursive(n::Node)
# Here we are doing something...
print(n.ID, " ")
for child in n.children
DFS_recursive(child)
end
end
// Simple recursive scheme for DFS
void dfs_recursive(node const& n) {
// Here we are doing something...
std::cout << n.value << ' ';
for (auto const& child : n.children) {
dfs_recursive(child);
}
}
private void DFSRecursive(Tree tree) {
Console.Write(tree.Id + " ");
foreach (var c in tree._children)
DFSRecursive(c);
}
public void DFSRecursive()
{
DFSRecursive(this);
}
void dfs_recursive(struct node n) {
printf("%d ", n.id);
if (n.children) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < n.children_size; ++i) {
dfs_recursive(n.children[i]);
}
}
}
private void dfsRecursive(Node node) {
System.out.print(node.id + " ");
for (Node n : node.children) {
dfsRecursive(n);
}
}
function dfsPreorder(tree) {
if (!tree) {
return;
}
process.stdout.write(tree.id + " ");
tree.children.forEach(dfsPreorder);
}
def dfs_recursive(node):
if node.data != None:
print(node.data, end=' ')
for child in node.children:
dfs_recursive(child)
fn dfs_recursive(n: &Node) {
print!("{} ", n.value);
for child in &n.children {
dfs_recursive(child);
}
}
dfs :: Tree a -> [a]
dfs (Node x ts) = x : concatMap dfs ts
func dfsRecursive(node: Node) {
print(node.value, terminator:" ")
for child in node.children! {
dfsRecursive(node: child)
}
}
public static function DFSRecursive(Tree $tree): void
{
echo $tree->getId() . ' ';
foreach ($tree->getChildren() as $child) {
static::DFSRecursive($child);
}
}
def dfs_recursive(node)
print "#{node.id} "
node.children.each{ |child| dfs_recursive child }
end
Node>>dfsRecursive
"Recursive depth first search."
Transcript show: data; cr.
children collect: [ :child | child dfsRecursive ]
Node>>dfsRecursivePostOrder
func dfsRecursive(n *node) {
fmt.Printf("%d ", n.id)
for _, child := range n.children {
dfsRecursive(child)
}
}
# rdi - children ptr
# rsi - value|children_size
dfs_recursive:
push r12
push r13
mov r12, rdi
mov r13, rsi
mov rdi, OFFSET fmt_tree # Handle the current node
shr rsi, 32 # The tree value is in the upper 32 bits
xor rax, rax
call printf
mov r13d, r13d # Zero out the top 32 bits
add r13, r12 # Pointer pointing after the last element of the children array
dfs_recursive_children:
cmp r12, r13 # If we reached the end, return
je dfs_recursive_return
mov rdi, QWORD PTR [r12]
mov rsi, QWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
call dfs_recursive
add r12, tree_size
jmp dfs_recursive_children
dfs_recursive_return:
pop r13
pop r12
ret
🌌🐕 depth_count children_count❗️
🍉
❗️ 🆔 ➡️ 🔢 🍇
↩️ id
🍉
❗️ 🧒 ➡️ 🍨🐚🌲🍆 🍇
(defun dfs-recursive (node)
"A depth first approach for printing out all values in a tree."
(when (node-data node)
(format t "~a " (node-data node)))
(loop for child in (node-children node) do
(dfs-recursive child)))
function DFS_recursive(n)
cell_index = @(a, b) a{b};
ID = cell_index(keys(n), 1);
fprintf('%u ', ID);
children = cell_index(values(n), 1);
for i = children
child = i{1};
if ~isempty(child)
DFS_recursive(child);
end
end
end
def dfs_recursive(Node(value, children)):
"""A depth first approach for printing out all values in a tree."""
print(value, end=' ')
for child in children:
dfs_recursive(child)
At least to me, this makes a lot of sense. We fight recursion with recursion! First, we first output the node we are on and then we call DFS_recursive(...) on each of its children nodes. This method of tree traversal does what its name implies: it goes to the depths of the tree first before going through the rest of the branches. In this case, the ordering looks like:
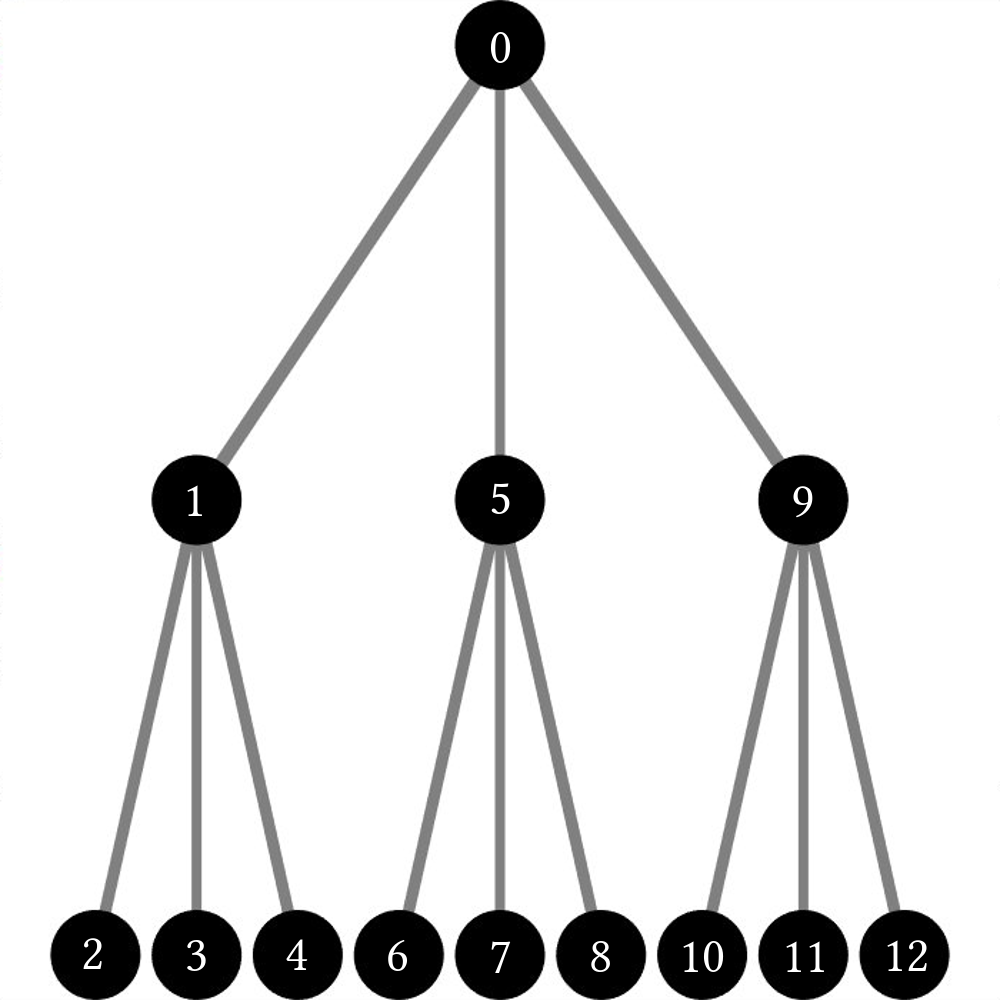
Note that the in the code above, we are missing a crucial step: checking to see if the node we are using actually exists! Because we are using a vector to store all the nodes, we will be careful not to run into a case where we call DFS_recursive(...) on a node that has yet to be initialized; however, depending on the language we are using, we might need to be careful of this to avoid recursion errors!
Now, in this case the first element searched through is still the root of the tree. This type of tree traversal is known as pre-order DFS. We perform an action (output the ID) before searching through the children. If we shift the function around and place the data output at the end of the function, we can modify the order in which we search through the tree to be post-order and look something like this:
function DFS_recursive_postorder(n::Node)
for child in n.children
DFS_recursive_postorder(child)
end
# Here we are doing something...
print(n.ID, " ")
end
void dfs_recursive_postorder(node const& n) {
for (auto const& child : n.children) {
dfs_recursive_postorder(child);
}
std::cout << n.value << ' ';
}
private void DFSRecursivePostorder(Tree tree)
{
foreach (var c in tree._children)
DFSRecursivePostorder(c);
Console.Write(tree.Id + " ");
}
public void DFSRecursivePostorder()
{
DFSRecursivePostorder(this);
void dfs_recursive_postorder(struct node n) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < n.children_size; ++i) {
dfs_recursive_postorder(n.children[i]);
}
printf("%d ", n.id);
}
private void dfsRecursivePostOrder(Node node) {
for (Node n : node.children) {
dfsRecursivePostOrder(n);
}
// Here we are doing something ...
System.out.print(node.id + " ");
}
function dfsPostorder(tree) {
if (!tree) {
return;
}
tree.children.forEach(dfsPostorder);
process.stdout.write(tree.id + " ");
}
def dfs_recursive_postorder(node):
for child in node.children:
dfs_recursive_postorder(child)
if node.data != None:
print(node.data, end=' ')
fn dfs_recursive_postorder(n: &Node) {
for child in &n.children {
dfs_recursive_postorder(child);
}
print!("{} ", n.value);
}
dfsPostOrder :: Tree a -> [a]
dfsPostOrder (Node x ts) = concatMap dfsPostOrder ts ++ [x]
func dfsRecursivePostOrder(node: Node) {
for child in node.children! {
dfsRecursivePostOrder(node: child)
}
print(node.value, terminator:" ")
}
public static function DFSRecursivePostorder(Tree $tree): void
{
foreach ($tree->getChildren() as $child) {
static::DFSRecursivePostorder($child);
}
echo $tree->getId() . ' ';
}
def dfs_recursive_postorder(node)
node.children.each{ |child| dfs_recursive_postorder child }
print "#{node.id} "
end
children collect: [ :child | (child dfsRecursivePostOrder)].
Transcript show: data; cr.
Node>>dfsInOrderBinaryTree
"Recursive depth first search on a binary tree in order."
children size > 2 ifTrue: [
func dfsRecursivePostorder(n *node) {
for _, child := range n.children {
dfsRecursivePostorder(child)
}
fmt.Printf("%d ", n.id)
}
# rdi - children ptr
# rsi - value|children_size
dfs_recursive_postorder:
push r12
push r13
push r14
mov r12, rdi
mov r13, rsi
mov r14, rsi
mov r13d, r13d # Zero out the top 32 bits
add r13, r12 # Pointer pointing after the last element of the children array
dfs_recursive_po_children:
cmp r12, r13 # If we reached the end, return
je dfs_recursive_po_return
mov rdi, QWORD PTR [r12]
mov rsi, QWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
call dfs_recursive_postorder
add r12, tree_size
jmp dfs_recursive_po_children
dfs_recursive_po_return:
mov rdi, OFFSET fmt_tree # Handle the current node
mov rsi, r14
shr rsi, 32 # The tree value is in the upper 32 bits
xor rax, rax
call printf
pop r14
pop r13
pop r12
ret
🍉
📗 Depth-First Search Recursive pre-order 📗
❗️ 🌀 🍇
😀 🔡 id 10❗️❗️
🔂 child children 🍇
🌀 child❗️
(defun dfs-recursive-postorder (node)
"A depth first approach for printing out all values in a tree starting from the bottom."
(loop for child in (node-children node) do
(dfs-recursive-postorder child))
(when (node-data node)
(format t "~a " (node-data node))))
function DFS_recursive_postorder(n)
cell_index = @(a, b) a{b};
children = cell_index(values(n), 1);
for i = children
child = i{1};
if ~isempty(child)
DFS_recursive_postorder(child);
end
end
ID = cell_index(keys(n), 1);
fprintf('%u ', ID);
end
def dfs_recursive_postorder(Node(value, children)):
"""A depth first approach for printing out all values in a tree starting from the bottom."""
for child in children:
dfs_recursive_postorder(child)
print(value, end=' ')
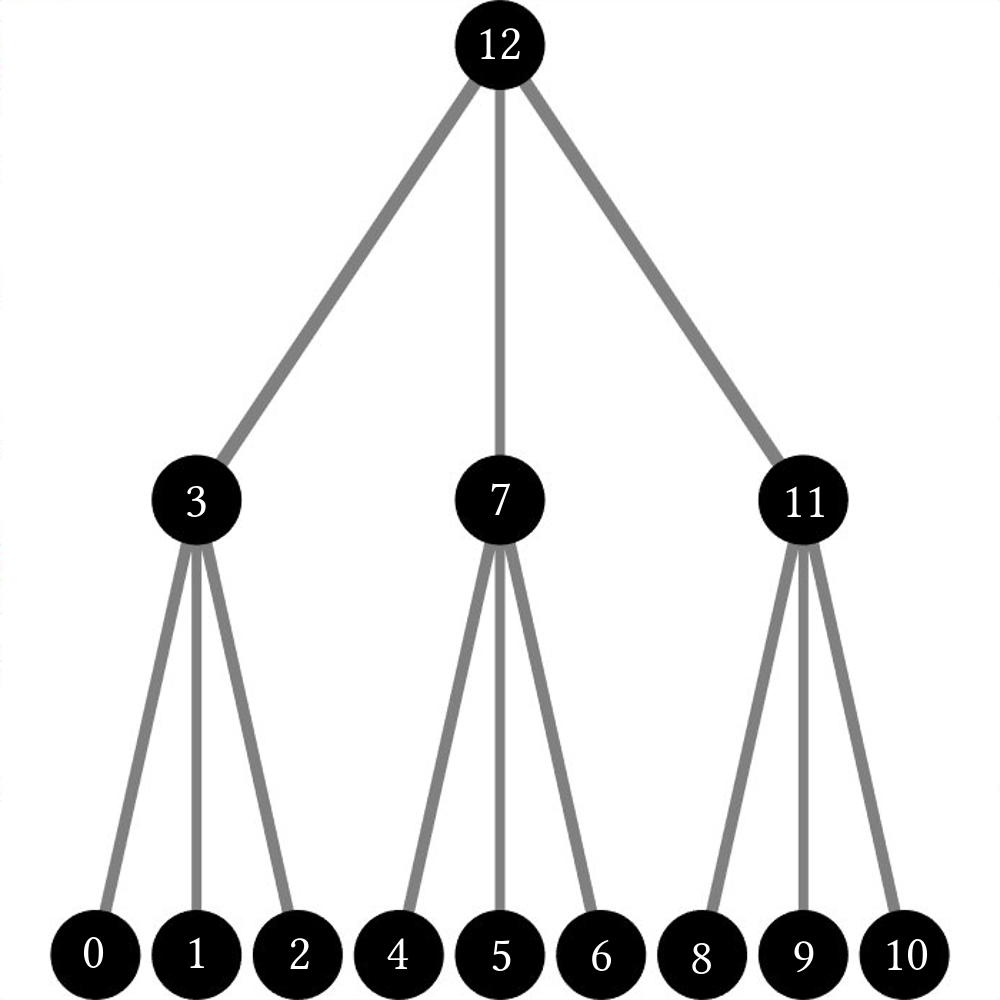
In this case, the first node visited is at the bottom of the tree and moves up the tree branch by branch. In addition to these two types, binary trees have an in-order traversal scheme that looks something like this:
# This assumes only 2 children, but accounts for other possibilities
function DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(n::Node)
if (length(n.children) == 2)
DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[1])
print(n.ID, " ")
DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[2])
elseif (length(n.children) == 1)
DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[1])
print(n.ID, " ")
elseif (length(n.children) == 0)
print(n.ID, " ")
else
println("Not a binary tree!")
end
end
void dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(node const& n) {
switch (n.children.size()) {
case 2:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[0]);
std::cout << n.value << ' ';
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[1]);
break;
case 1:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[0]);
std::cout << n.value << ' ';
break;
case 0:
std::cout << n.value << ' ';
break;
default:
std::cout << "This is not a binary tree.\n";
break;
}
}
private void DFSRecursiveInorderBinary(Tree tree)
{
switch (tree._children.Count)
{
case 2:
DFSRecursiveInorderBinary(tree._children[0]);
Console.Write(tree.Id + " ");
DFSRecursiveInorderBinary(tree._children[1]);
break;
case 1:
DFSRecursiveInorderBinary(tree._children[0]);
Console.Write(tree.Id + " ");
break;
case 0:
Console.Write(tree.Id + " ");
break;
default:
throw new Exception("Not binary tree!");
}
}
public void DFSRecursiveInorderBinary()
{
DFSRecursiveInorderBinary(this);
void dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(struct node n) {
switch (n.children_size) {
case 2:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[0]);
printf("%d ", n.id);
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[1]);
break;
case 1:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[0]);
printf("%d ", n.id);
break;
case 0:
printf("%d ", n.id);
break;
default:
printf("This is not a binary tree.\n");
break;
}
}
private void dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(Node node) {
switch (node.children.size()) {
case 2:
dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(node.children.get(0));
System.out.print(node.id + " ");
dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(node.children.get(1));
break;
case 1:
dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(node.children.get(0));
System.out.print(node.id + " ");
break;
case 0:
System.out.print(node.id + " ");
break;
default:
System.err.println("Not a binary tree at dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary()!");
}
}
function dfsInorder(tree) {
if (!tree) {
return;
}
switch (tree.children.length) {
case 2:
dfsInorder(tree.children[0]);
console.log(tree.id);
dfsInorder(tree.children[1]);
break;
case 1:
dfsInorder(tree.children[0]);
console.log(tree.id);
break;
case 0:
console.log(tree.id);
break;
default:
throw new Error("Postorder traversal is only valid for binary trees");
}
}
def dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(node):
if len(node.children) == 2:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(node.children[0])
print(node.data, end=' ')
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(node.children[1])
elif len(node.children) == 1:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(node.children[0])
print(node.data, end=' ')
elif len(node.children) == 0:
print(node.data, end=' ')
else:
print("Not a binary tree!")
fn dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(n: &Node) {
match &n.children[..] {
[left, right] => {
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(left);
print!("{} ", n.value);
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(right);
}
[left] => {
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(left);
print!("{} ", n.value);
}
[] => print!("{} ", n.value),
_ => print!("This is not a binary tree. "),
}
}
dfsInOrder :: Tree a -> [a] -- For binary trees only
dfsInOrder (Node x []) = [x]
dfsInOrder (Node x [l]) = dfsInOrder l ++ [x] -- Single branch assumed to be left
dfsInOrder (Node x [l, r]) = dfsInOrder l ++ [x] ++ dfsInOrder r
dfsInOrder _ = error "Not a binary tree"
func dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(node: Node) {
if node.children?.count == 2 {
dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(node: node.children![0])
print(node.value, terminator:" ")
dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(node: node.children![1])
} else if node.children?.count == 1 {
dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(node: node.children![0])
print(node.value, terminator:" ")
} else if node.children?.count == 0 {
print(node.value, terminator:" ")
} else {
print("Not a binary tree!")
}
}
public static function DFSRecursiveInorderBinary(Tree $tree): void
{
switch (count($tree->getChildren())) {
case 2:
static::DFSRecursiveInorderBinary($tree->getChildren()[0]);
echo $tree->getId() . ' ';
static::DFSRecursiveInorderBinary($tree->getChildren()[1]);
break;
case 1:
static::DFSRecursiveInorderBinary($tree->getChildren()[0]);
echo $tree->getId() . ' ';
break;
case 0:
echo $tree->getId() . ' ';
break;
default:
throw new InvalidArgumentException('Not a binary tree!');
break;
}
}
def dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(node)
case node.children.size
when 2
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree node.children[0]
print "#{node.id} "
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree node.children[1]
when 1
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree node.children[0]
print "#{node.id} "
when 0
print "#{node.id} "
else
print "Not a binary tree!"
end
end
^self.
].
children size = 2 ifTrue: [
(children at: 1) dfsInOrderBinaryTree: value.
].
Transcript show: data; cr.
children size >= 1 ifTrue: [
(children at: 0) dfsInOrderBinaryTree: value.
].
^self.
Node>>dfsStack
"Depth-first search with a stack."
| stack top |
func dfsRecursiveInorderBtree(n *node) {
switch len(n.children) {
case 2:
dfsRecursiveInorderBtree(n.children[0])
fmt.Printf("%d ", n.id)
dfsRecursiveInorderBtree(n.children[1])
case 1:
dfsRecursiveInorderBtree(n.children[0])
fmt.Printf("%d ", n.id)
case 0:
fmt.Printf("%d ", n.id)
default:
fmt.Println("This is not a binary tree")
}
}
# rdi - children ptr
# rsi - value|children_size
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree:
push r12
push r13
mov r12, rdi
mov r13, rsi
mov rax, rsi
mov eax, eax
cmp rax, 0 # Check what type of tree it is.
je dfs_recursive_bt_size0
cmp rax, 16
je dfs_recursive_bt_size1
cmp rax, 32
je dfs_recursive_bt_size2
mov rdi, OFFSET not_bt # If the tree is not binary then print a warning
xor rax, rax
call printf
jmp dfs_recursive_bt_return
dfs_recursive_bt_size0:
mov rdi, OFFSET fmt_tree # If the node is a leaf then print its id
shr rsi, 32
xor rax, rax
call printf
jmp dfs_recursive_bt_return
dfs_recursive_bt_size1:
mov rdi, QWORD PTR [r12] # If the node has 1 child then call the function and print the id
mov rsi, QWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
call dfs_recursive_inorder_btree
mov rdi, OFFSET fmt_tree
mov rsi, r13
shr rsi, 32
xor rax, rax
call printf
jmp dfs_recursive_bt_return
dfs_recursive_bt_size2:
mov rdi, QWORD PTR [r12] # Same as above just print id inbetween the calls
mov rsi, QWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
call dfs_recursive_inorder_btree
mov rdi, OFFSET fmt_tree
mov rsi, r13
shr rsi, 32
xor rax, rax
call printf
mov rdi, QWORD PTR [r12 + 16]
mov rsi, QWORD PTR [r12 + 24]
call dfs_recursive_inorder_btree
dfs_recursive_bt_return:
pop r13
pop r12
ret
🍉
📗 Depth-First Search Recursive post-order 📗
❗️ 🍥 🍇
🔂 child children 🍇
🍥 child❗️
🍉
😀 🔡 id 10❗️❗️
🍉
📗
Depth-First Search Recursive Inorder Binary
This assumes only 2 children.
📗
❗️ 🍭 ➡️ 🍬⏹ 🍇
↪️ 🐔 children❗️ ▶️ 2 🍇
↩️ 🆕⏹⏫❗️
(defun dfs-recursive-inorder-btree (node)
"A depth first search approach for printing all values in a binary tree."
(case (length (node-children node))
(2
(dfs-recursive-inorder-btree (first (node-children node)))
(format t "~a " (node-data node))
(dfs-recursive-inorder-btree (second (node-children node))))
(1
(dfs-recursive-inorder-btree (first (node-children node)))
(format t "~a " (node-data node)))
(0
(format t "~a " (node-data node)))
(t
(print "Invalid binary tree."))))
function DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(n)
cell_index = @(a, b) a{b};
ID = cell_index(keys(n), 1);
children = cell_index(values(n), 1);
if length(children) == 2
DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(children{1})
fprintf('%u ', ID)
DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(children{2})
elseif length(children) == 1
if ~isempty(children{1})
DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(children{1})
end
fprintf('%u ', ID)
else
fprintf("Not a binary tree!")
end
end
def dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(Node(value, children)):
"""A depth first search approach for printing all values in a binary tree."""
match len(children):
case 2:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(children[0])
print(value, end=' ')
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(children[1])
case 1:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(children[0])
print(value, end=' ')
case 0:
print(value, end=' ')
else:
print('Invalid binary tree')
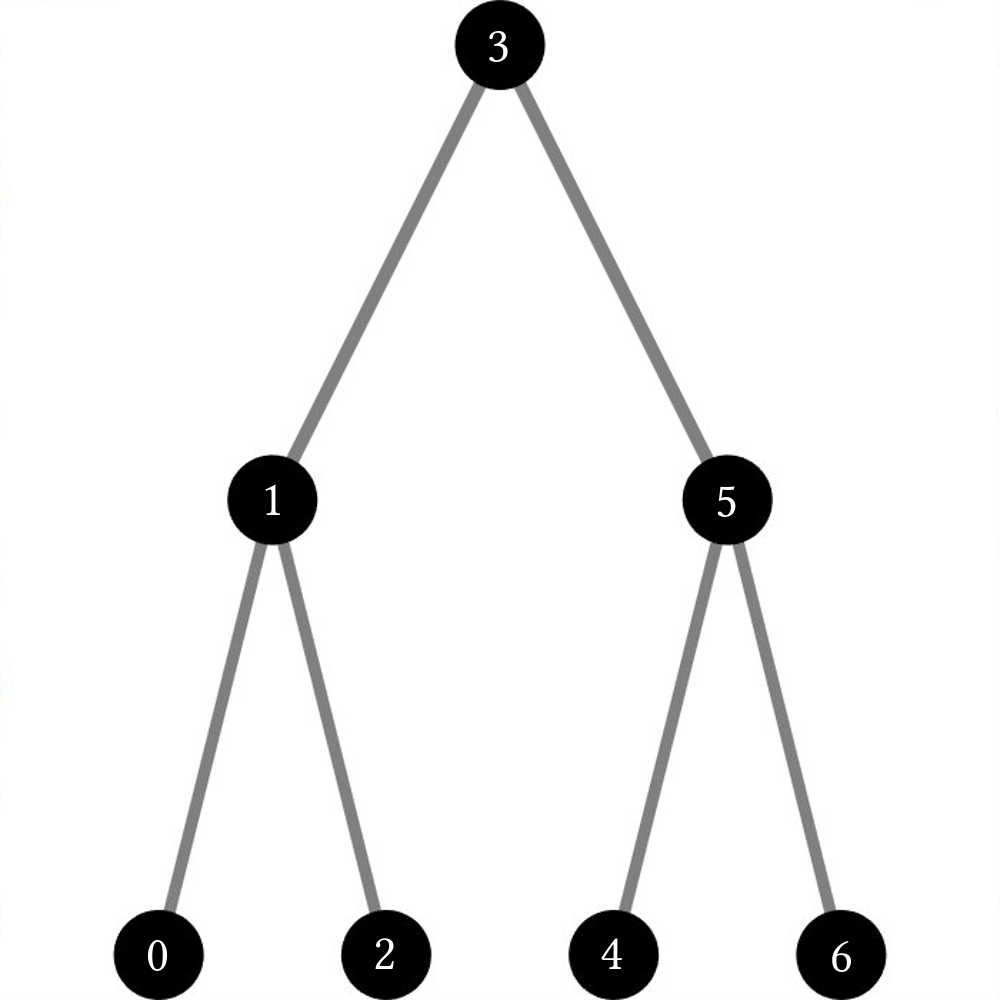
The order here seems to be some mix of the other 2 methods and works through the binary tree from left to right.
Now, at this point, it might seem that the only way to search through a recursive data structure is with recursion, but this is not necessarily the case! Rather surprisingly, we can perform a DFS non-recursively by using a stack, which are data structures that hold multiple elements, but only allow you to interact with the very last element you put in. The idea here is simple:
- Put the root node in the stack
- Take it out and put in its children
- Pop the top of the stack and put its children in
- Repeat 3 until the stack is empty
In code, it looks like this:
function DFS_stack(n::Node)
s = Stack{Node}()
push!(s, n)
while(length(s) > 0)
print(top(s).ID, " ")
temp = pop!(s)
for child in temp.children
push!(s, child)
end
end
end
void dfs_stack(node const& n) {
// this stack holds pointers into n's `children` vector,
// or its children's `children` vector.
std::stack<node const*> stack;
stack.push(&n);
while (stack.size() > 0) {
auto const& temp = *stack.top();
stack.pop();
std::cout << temp.value << ' ';
for (auto const& child : temp.children) {
stack.push(&child);
}
}
}
}
public void DFSStack()
{
var stack = new Stack<Tree>();
stack.Push(this);
while (stack.Count != 0)
{
Console.Write(stack.Peek().Id + " ");
var temp = stack.Pop();
foreach (var c in temp._children)
stack.Push(c);
void dfs_stack(struct node n) {
struct stack stk = get_stack(sizeof(struct node*));
stack_push(&stk, &n);
struct node *tmp;
while (!stack_empty(&stk)) {
tmp = (struct node*)stack_pop(&stk);
if (!tmp) {
break;
}
printf("%d ", tmp->id);
for (size_t i = 0; i < tmp->children_size; ++i) {
stack_push(&stk, &tmp->children[i]);
}
}
free_stack(stk);
}
public void dfsStack() {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
stack.push(this.root);
Node tmp;
while (stack.size() != 0) {
System.out.print(stack.peek().id + " ");
tmp = stack.pop();
for (Node c : tmp.children) {
stack.push(c);
}
}
}
function dfsIterative(tree) {
const stack = [tree];
while (stack.length > 0) {
const current = stack.pop();
process.stdout.write(current.id + " ");
stack.push(...current.children);
}
}
def dfs_stack(node):
stack = [node]
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
stack.extend(node.children)
print(node.data, end=' ')
fn dfs_stack(n: &Node) {
let mut stack = vec![n];
while let Some(current) = stack.pop() {
print!("{} ", current.value);
stack.extend(¤t.children);
}
}
dfsStack :: Tree a -> [a]
dfsStack t = go [t]
where
go [] = []
go ((Node x ts) : stack) = x : go (ts ++ stack)
func dfsStack(node: Node) {
var stack = [node]
var temp: Node
while stack.count > 0 {
temp = stack.popLast()!
print(temp.value, terminator:" ")
for child in temp.children! {
stack.append(child)
}
}
}
public static function DFSStack(Tree $tree): void
{
$stack = [$tree];
$temp = null;
while (null !== ($temp = array_pop($stack))) {
echo $temp->getId() . ' ';
foreach ($temp->getChildren() as $child) {
$stack[] = $child;
}
}
}
def dfs_stack(node)
stack = [node]
until stack.empty?
temp = stack.pop
print "#{temp.id} "
temp.children.each{ |child| stack.push child }
end
end
Node>>dfsStack
"Depth-first search with a stack."
| stack top |
stack := Stack new.
stack push: self.
[stack size > 0] whileTrue: [
top := stack pop.
Transcript show: (top data); cr.
top children reverseDo: [ :child |
stack push: child.
].
].
func dfsStack(n *node) {
stack := []*node{n}
for len(stack) > 0 {
cur := stack[0]
stack = stack[1:]
fmt.Printf("%d ", cur.id)
stack = append(cur.children, stack...)
}
}
# rdi - children ptr
# rsi - value|children_size
dfs_stack:
push r12
push r13
push r14
sub rsp, 16 # Create stack
mov r12, rsp
push rsi # Save node to use as pointer
push rdi
mov rdi, r12
call get_stack # Init stack
mov rdi, r12
mov rsi, rsp
call stack_push # Push node
mov rdi, r12 # Pop stack
call stack_pop
dfs_stack_loop:
test rax, rax # Test if stack is empty
jz dfs_stack_return
mov r13, rax
mov rdi, OFFSET fmt_tree # Print id
mov esi, DWORD PTR [r13 + 12]
xor rax, rax
call printf
mov eax, DWORD PTR [r13 + 8] # Get start and end of array
mov r13, QWORD PTR [r13]
lea r14, [r13 + rax]
dfs_stack_push_child:
cmp r13, r14 # Check if the pointers are the same
je dfs_stack_end_push
mov rdi, r12 # Push node into the stack
mov rsi, r13
call stack_push
add r13, tree_size
jmp dfs_stack_push_child
dfs_stack_end_push:
mov rdi, r12 # Pop stack
call stack_pop
jmp dfs_stack_loop
dfs_stack_return:
mov rdi, r12 # Free stack
call free_stack
add rsp, 32
pop r14
pop r13
pop r12
ret
↪️ 🐔 children❗️ ▶️ 0 🍇
🍭🐽 children 0❗️❗️
😀 🔡 id 10❗️❗️
🍭🐽 children 1❗️❗️
🍉
🙅 🍇
😀 🔡 id 10❗️❗️
🍉
↩️ 🤷♀️
🍉
📗 Depth-First Search Stack 📗
❗️ 🥞 🍇
🍨 🐕 🍆 ➡️ stack
(defun dfs-stack (node)
"A depth first approach for printing out all values in a tree using a stack."
(loop
with stack = (list node)
with temp = nil
while (> (length stack) 0) do
(format t "~a " (node-data (first stack)))
(setf temp (pop stack))
(loop for child in (node-children temp) do
(push child stack))))
function DFS_stack(n)
cell_index = @(a, b) a{b};
node_stack = {n};
while ~isempty(node_stack)
parent = node_stack{end};
node_stack(end) = [];
ID = cell_index(keys(parent), 1);
fprintf('%u ', ID);
children = cell_index(values(parent), 1);
for i = flip(children)
child = i{1};
if ~isempty(child)
node_stack = {node_stack{:} child};
end
end
end
end
def dfs_stack(Node(node)):
"""A depth first approach for printing out all values in a tree using a stack."""
stack = [node]
while stack:
current_node = stack.pop()
print(current_node.value, end=' ')
for child in current_node.children:
stack.append(child)
All this said, there are a few details about DFS that might not be ideal, depending on the situation. For example, if we use DFS on an incredibly long tree, we will spend a lot of time going further and further down a single branch without searching the rest of the data structure. In addition, it is not the natural way humans would order a tree if asked to number all the nodes from top to bottom. I would argue a more natural traversal order would look something like this:
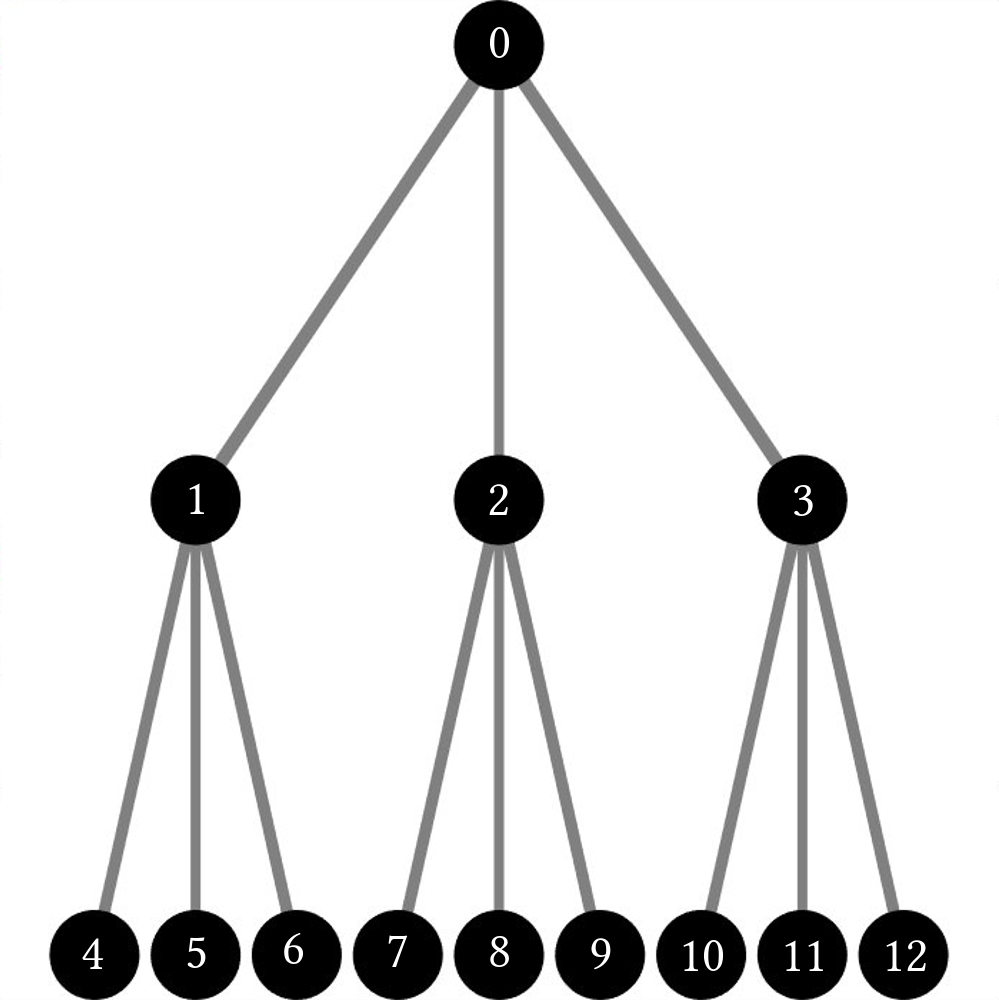
And this is exactly what Breadth-First Search (BFS) does! On top of that, it can be implemented in the same way as the DFS_stack(...) function above, simply by swapping the stack for a queue, which is similar to a stack, except that it only allows you to interact with the very first element instead of the last. In code, this looks something like:
function BFS_queue(n::Node)
q = Queue{Node}()
enqueue!(q, n)
while(length(q) > 0)
print(first(q).ID, " ")
temp = dequeue!(q)
for child in temp.children
enqueue!(q, child)
end
end
end
void bfs_queue(node const& n) {
std::queue<node const*> queue;
queue.push(&n);
while (queue.size() > 0) {
auto const& temp = *queue.front();
queue.pop();
std::cout << temp.value << ' ';
for (auto const& child : temp.children) {
queue.push(&child);
}
}
}
}
public void BFSQueue()
{
var queue = new Queue<Tree>();
queue.Enqueue(this);
while (queue.Count != 0)
{
Console.Write(queue.Peek().Id + " ");
var temp = queue.Dequeue();
foreach (var c in temp._children)
queue.Enqueue(c);
void bfs_queue(struct node n) {
struct queue q = get_queue(sizeof(struct node*));
enqueue(&q, &n);
struct node *tmp;
while (!queue_empty(&q)) {
tmp = (struct node*)dequeue(&q);
if (!tmp) {
break;
}
printf("%d ", tmp->id);
for (size_t i = 0; i < tmp->children_size; ++i) {
enqueue(&q, &tmp->children[i]);
}
}
free_queue(q);
}
public void bfsQueue() {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
queue.add(this.root);
while (queue.size() != 0) {
System.out.print(queue.peek().id + " ");
Node temp = queue.poll(); // return null if the queue is empty
if (temp != null) {
for (Node c : temp.children) {
queue.add(c);
}
}
}
}
function bfs(tree) {
const queue = [tree];
while (queue.length > 0) {
const current = queue.shift();
process.stdout.write(current.id + " ");
queue.push(...current.children);
}
}
def bfs_queue(node):
queue = [node]
while queue:
node = queue.pop(0)
queue.extend(node.children)
print(node.data)
fn bfs_queue(n: &Node) {
let mut queue = VecDeque::new();
queue.push_back(n);
while let Some(current) = queue.pop_front() {
print!("{} ", current.value);
queue.extend(¤t.children);
}
}
bfs :: Tree a -> [a]
bfs (Node x ts) = x : go ts
where
go [] = []
go ts = map node ts ++ go (concatMap forest ts)
func bfsQueue(node: Node) {
var queue = [node]
var temp: Node
while queue.count > 0 {
temp = queue.remove(at: 0)
print(temp.value, terminator:" ")
for child in temp.children! {
queue.append(child)
}
}
}
public static function DFSQueue(Tree $tree): void
{
$stack = [$tree];
$temp = null;
while (null !== ($temp = array_shift($stack))) {
echo $temp->getId() . ' ';
foreach ($temp->getChildren() as $child) {
$stack[] = $child;
}
}
}
def bfs_queue(node)
queue = Deque.new [node]
until queue.empty?
temp = queue.shift
print "#{temp.id} "
temp.children.each{ |child| queue.push child }
end
end
Node>>bfs
"A breadth-first tree search using queues."
| queue current |
queue := LinkedList with: self.
[ queue size > 0 ] whileTrue: [
current := queue first.
queue removeFirst.
Transcript show: (current data); cr.
current children collect: [ :child |
queue addLast: child
].
].
func bfsQueue(n *node) {
queue := []*node{n}
for len(queue) > 0 {
cur := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
fmt.Printf("%d ", cur.id)
queue = append(queue, cur.children...)
}
}
# rdi - children ptr
# rsi - value|children_size
bfs_queue:
push r12
push r13
push r14
sub rsp, 20 # Create queue
mov r12, rsp
push rsi # Save node to use as pointer
push rdi
mov rdi, r12
call get_queue # Init queue
mov rdi, r12
mov rsi, rsp
call enqueue # enqueue node
mov eax, DWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
mov edi, DWORD PTR [r12 + 12]
bfs_queue_loop:
cmp eax, edi
je bfs_queue_return
mov rdi, r12 # dequeue
call dequeue
test rax, rax # Test if queue is empty
jz bfs_queue_return
mov r13, rax
mov rdi, OFFSET fmt_tree # Print id
mov esi, DWORD PTR [r13 + 12]
xor rax, rax
call printf
mov eax, DWORD PTR [r13 + 8] # Get start and end of array
mov r13, QWORD PTR [r13]
lea r14, [r13 + rax]
bfs_queue_push_child:
cmp r13, r14 # Check if the pointers are the same
je bfs_queue_end_push
mov rdi, r12 # enqueue node
mov rsi, r13
call enqueue
add r13, tree_size
jmp bfs_queue_push_child
bfs_queue_end_push:
mov eax, DWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
mov edi, DWORD PTR [r12 + 12]
jmp bfs_queue_loop
bfs_queue_return:
mov rdi, r12 # Free queue
call free_queue
add rsp, 36
pop r14
pop r13
pop r12
ret
🐽 stack 🐔 stack❗️ ➖ 1❗️ ➡️ temp
🐨 stack 🐔 stack❗️ ➖ 1❗️
😀 🔡 🆔 temp❗️ 10❗️❗️
🧒 temp❗️ ➡️ temp_children
🔂 child temp_children 🍇
🐻 stack child❗️
🍉
🍉
🍉
📗 Breadth-First Search Queue 📗
❗️ 🏢 🍇
🍨 🐕 🍆 ➡️ queue
(defun bfs-queue (node)
"A breadth first search approach for printing out all values in a tree."
(loop
with queue = (list node)
with temp = nil
while (> (length queue) 0) do
(format t "~a " (node-data (first queue)))
(setf temp (pop queue))
;; If the queue is empty, the queue should be filled with the children nodes.
(if (eql queue nil)
(setf queue (node-children temp))
(nconc queue (node-children temp)))))
function BFS_queue(n)
cell_index = @(a, b) a{b};
node_queue = {n};
while ~isempty(node_queue)
next_nodes = {};
for parent_cell = node_queue
parent = parent_cell{1};
ID = cell_index(keys(parent), 1);
fprintf('%u ', ID);
children = cell_index(values(parent), 1);
for i = children
child = i{1};
if ~isempty(child)
next_nodes = {next_nodes{:}, child};
end
end
end
node_queue = next_nodes;
end
end
def bfs_queue(Node(node)):
"""A breadth first search approach for printing out all values in a tree."""
queue = deque([node])
while queue:
current_node = queue.popleft()
print(current_node.value, end=' ')
for child in current_node.children:
queue.append(child)
Video Explanation
Here is a video describing tree traversal:
Example Code
using DataStructures, Printf
struct Node
children::Vector{Node}
ID::Int64
Node(ID::Int64) = new(Vector{Node}(), ID)
end
function DFS_recursive(n::Node)
# Here we are doing something...
print(n.ID, " ")
for child in n.children
DFS_recursive(child)
end
end
function DFS_recursive_postorder(n::Node)
for child in n.children
DFS_recursive_postorder(child)
end
# Here we are doing something...
print(n.ID, " ")
end
# This assumes only 2 children, but accounts for other possibilities
function DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(n::Node)
if (length(n.children) == 2)
DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[1])
print(n.ID, " ")
DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[2])
elseif (length(n.children) == 1)
DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[1])
print(n.ID, " ")
elseif (length(n.children) == 0)
print(n.ID, " ")
else
println("Not a binary tree!")
end
end
function DFS_stack(n::Node)
s = Stack{Node}()
push!(s, n)
while(length(s) > 0)
print(top(s).ID, " ")
temp = pop!(s)
for child in temp.children
push!(s, child)
end
end
end
function BFS_queue(n::Node)
q = Queue{Node}()
enqueue!(q, n)
while(length(q) > 0)
print(first(q).ID, " ")
temp = dequeue!(q)
for child in temp.children
enqueue!(q, child)
end
end
end
# function to create a simple, balanced tree
function create_tree(num_row::Int64, num_child::Int64)
ret = Node(num_row)
if (num_row == 0)
return ret
end
for i = 1:num_child
child = create_tree(num_row - 1, num_child)
push!(ret.children, child)
end
return ret
end
function main()
root = create_tree(2, 3)
println("[#]\nRecursive DFS:")
DFS_recursive(root);
println()
println("[#]\nRecursive Postorder DFS:")
DFS_recursive_postorder(root);
println()
println("[#]\nStack-based DFS:")
DFS_stack(root);
println()
println("[#]\nQueue-based BFS:")
BFS_queue(root);
println()
root_binary = create_tree(3,2)
println("[#]\nRecursive Inorder DFS for Binary Tree:")
DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(root_binary)
println()
end
main()
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstddef>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
using std::size_t;
struct node {
std::vector<node> children;
size_t value;
};
// Simple recursive scheme for DFS
void dfs_recursive(node const& n) {
// Here we are doing something...
std::cout << n.value << ' ';
for (auto const& child : n.children) {
dfs_recursive(child);
}
}
void dfs_recursive_postorder(node const& n) {
for (auto const& child : n.children) {
dfs_recursive_postorder(child);
}
std::cout << n.value << ' ';
}
void dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(node const& n) {
switch (n.children.size()) {
case 2:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[0]);
std::cout << n.value << ' ';
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[1]);
break;
case 1:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[0]);
std::cout << n.value << ' ';
break;
case 0:
std::cout << n.value << ' ';
break;
default:
std::cout << "This is not a binary tree.\n";
break;
}
}
// Simple non-recursive scheme for DFS
void dfs_stack(node const& n) {
// this stack holds pointers into n's `children` vector,
// or its children's `children` vector.
std::stack<node const*> stack;
stack.push(&n);
while (stack.size() > 0) {
auto const& temp = *stack.top();
stack.pop();
std::cout << temp.value << ' ';
for (auto const& child : temp.children) {
stack.push(&child);
}
}
}
// simple non-recursive scheme for BFS
void bfs_queue(node const& n) {
std::queue<node const*> queue;
queue.push(&n);
while (queue.size() > 0) {
auto const& temp = *queue.front();
queue.pop();
std::cout << temp.value << ' ';
for (auto const& child : temp.children) {
queue.push(&child);
}
}
}
node create_tree(size_t num_row, size_t num_child) {
if (num_row == 0) {
return node{std::vector<node>(), 0};
}
std::vector<node> vec;
std::generate_n(std::back_inserter(vec), num_child, [&] {
return create_tree(num_row - 1, num_child);
});
return node{std::move(vec), num_row};
}
int main() {
// Creating Tree in main
auto root = create_tree(2, 3);
auto binary_root = create_tree(3, 2);
std::cout << "[#]\nRecursive DFS:\n";
dfs_recursive(root);
std::cout << '\n';
std::cout << "[#]\nRecursive Postorder DFS:\n";
dfs_recursive_postorder(root);
std::cout << '\n';
std::cout << "[#]\nStack-based DFS:\n";
dfs_stack(root);
std::cout << '\n';
std::cout << "[#]\nQueue-based BFS:\n";
bfs_queue(root);
std::cout << '\n';
std::cout << "[#]\nRecursive Inorder DFS for Binary Tree:\n";
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(binary_root);
std::cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
Tree.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace TreeTraversal
{
public class Tree
{
public int Id { get; private set; }
private List<Tree> _children = new List<Tree>();
public Tree(int depthCount, int childrenCount)
{
Id = 1;
if (depthCount > 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < childrenCount; i++)
_children.Add(new Tree(Id * 10 + i + 1, depthCount - 1, childrenCount));
}
}
private Tree(int id, int depthCount, int childrenCount)
{
Id = id;
if (!(depthCount <= 1))
{
for (int i = 0; i < childrenCount; i++)
_children.Add(new Tree(Id * 10 + i + 1, depthCount - 1, childrenCount));
}
}
private void DFSRecursive(Tree tree) {
Console.Write(tree.Id + " ");
foreach (var c in tree._children)
DFSRecursive(c);
}
public void DFSRecursive()
{
DFSRecursive(this);
}
private void DFSRecursivePostorder(Tree tree)
{
foreach (var c in tree._children)
DFSRecursivePostorder(c);
Console.Write(tree.Id + " ");
}
public void DFSRecursivePostorder()
{
DFSRecursivePostorder(this);
}
private void DFSRecursiveInorderBinary(Tree tree)
{
switch (tree._children.Count)
{
case 2:
DFSRecursiveInorderBinary(tree._children[0]);
Console.Write(tree.Id + " ");
DFSRecursiveInorderBinary(tree._children[1]);
break;
case 1:
DFSRecursiveInorderBinary(tree._children[0]);
Console.Write(tree.Id + " ");
break;
case 0:
Console.Write(tree.Id + " ");
break;
default:
throw new Exception("Not binary tree!");
}
}
public void DFSRecursiveInorderBinary()
{
DFSRecursiveInorderBinary(this);
}
public void DFSStack()
{
var stack = new Stack<Tree>();
stack.Push(this);
while (stack.Count != 0)
{
Console.Write(stack.Peek().Id + " ");
var temp = stack.Pop();
foreach (var c in temp._children)
stack.Push(c);
}
}
public void BFSQueue()
{
var queue = new Queue<Tree>();
queue.Enqueue(this);
while (queue.Count != 0)
{
Console.Write(queue.Peek().Id + " ");
var temp = queue.Dequeue();
foreach (var c in temp._children)
queue.Enqueue(c);
}
}
}
}
Program.cs
using System;
namespace TreeTraversal
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var tree = new Tree(2, 3);
Console.WriteLine("[#]\nRecursive DFS:");
tree.DFSRecursive();
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("[#]\nRecursive Postorder DFS:");
tree.DFSRecursivePostorder();
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("[#]\nStack-based DFS:");
tree.DFSStack();
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("[#]\nQueue-based BFS:");
tree.BFSQueue();
Console.WriteLine();
tree = new Tree(3, 2);
Console.WriteLine("[#]\nRecursive Inorder DFS for Binary Tree:");
tree.DFSRecursiveInorderBinary();
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
utility.h
#ifndef UTILITY_H
#define UTILITY_H
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct stack {
void **data;
size_t top, capacity, size;
};
struct queue {
void **data;
size_t front, back, capacity;
};
struct stack get_stack(size_t size) {
struct stack stk;
stk.data = malloc(4 * size);
stk.capacity = 4;
stk.top = 0;
return stk;
}
bool stack_empty(struct stack *stk) {
return stk->top == 0;
}
void stack_push(struct stack *stk, void *element) {
if (stk->top == stk->capacity) {
stk->capacity *= 2;
stk->data = realloc(stk->data, stk->capacity * sizeof(stk->data[0]));
}
stk->data[stk->top++] = element;
}
void *stack_pop(struct stack *stk) {
if (stack_empty(stk)) {
return NULL;
}
return stk->data[--stk->top];
}
void free_stack(struct stack stk) {
free(stk.data);
}
struct queue get_queue(size_t size) {
struct queue q;
q.data = calloc(4, size);
q.front = 0;
q.back = 0;
q.capacity = 4;
return q;
}
bool queue_empty(struct queue *q) {
return q->front == q->back;
}
void queue_resize(struct queue *q) {
size_t size = sizeof(q->data[0]);
void **tmp = calloc((q->capacity * 2), size);
memcpy(tmp, q->data + q->front, (q->capacity - q->front) * size);
memcpy(tmp + q->capacity - q->front, q->data, (q->front - 1) * size);
free(q->data);
q->data = tmp;
q->back = q->capacity - 1;
q->front = 0;
q->capacity *= 2;
}
void enqueue(struct queue *q, void *element) {
if (q->front == (q->back + 1) % q->capacity) {
queue_resize(q);
}
q->data[q->back] = element;
q->back = (q->back + 1) % q->capacity;
}
void *dequeue(struct queue *q) {
if (queue_empty(q)) {
return NULL;
}
void *ret = q->data[q->front];
q->front = (q->front + 1) % q->capacity;
return ret;
}
void free_queue(struct queue q) {
free(q.data);
}
#endif //UTILITY_H
tree_traversal.c
#include "utility.h"
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
struct node {
struct node *children;
size_t children_size;
int id;
};
struct node create_tree(int rows, size_t num_children) {
struct node n = {NULL, 0, rows};
if (rows > 0) {
n.children = (struct node*)malloc(num_children * sizeof(struct node));
n.children_size = num_children;
for (size_t i = 0; i < num_children; ++i) {
n.children[i] = create_tree(rows - 1, num_children);
}
}
return n;
}
void destroy_tree(struct node n) {
if (n.id > 0) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < n.children_size; ++i) {
destroy_tree(n.children[i]);
}
free(n.children);
}
}
void dfs_recursive(struct node n) {
printf("%d ", n.id);
if (n.children) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < n.children_size; ++i) {
dfs_recursive(n.children[i]);
}
}
}
void dfs_recursive_postorder(struct node n) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < n.children_size; ++i) {
dfs_recursive_postorder(n.children[i]);
}
printf("%d ", n.id);
}
void dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(struct node n) {
switch (n.children_size) {
case 2:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[0]);
printf("%d ", n.id);
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[1]);
break;
case 1:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(n.children[0]);
printf("%d ", n.id);
break;
case 0:
printf("%d ", n.id);
break;
default:
printf("This is not a binary tree.\n");
break;
}
}
void dfs_stack(struct node n) {
struct stack stk = get_stack(sizeof(struct node*));
stack_push(&stk, &n);
struct node *tmp;
while (!stack_empty(&stk)) {
tmp = (struct node*)stack_pop(&stk);
if (!tmp) {
break;
}
printf("%d ", tmp->id);
for (size_t i = 0; i < tmp->children_size; ++i) {
stack_push(&stk, &tmp->children[i]);
}
}
free_stack(stk);
}
void bfs_queue(struct node n) {
struct queue q = get_queue(sizeof(struct node*));
enqueue(&q, &n);
struct node *tmp;
while (!queue_empty(&q)) {
tmp = (struct node*)dequeue(&q);
if (!tmp) {
break;
}
printf("%d ", tmp->id);
for (size_t i = 0; i < tmp->children_size; ++i) {
enqueue(&q, &tmp->children[i]);
}
}
free_queue(q);
}
int main() {
struct node root = create_tree(2, 3);
printf("[#]\nRecursive DFS:\n");
dfs_recursive(root);
printf("\n");
printf("[#]\nRecursive Postorder DFS:\n");
dfs_recursive_postorder(root);
printf("\n");
printf("[#]\nStack-based DFS:\n");
dfs_stack(root);
printf("\n");
printf("[#]\nQueue-based BFS:\n");
bfs_queue(root);
printf("\n");
destroy_tree(root);
struct node root_binary = create_tree(3, 2);
printf("[#]\nRecursive Inorder DFS for Binary Tree:\n");
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(root_binary);
printf("\n");
destroy_tree(root_binary);
return 0;
}
Tree.java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Tree {
public Node root;
public Tree(int rowCount, int childrenCount) {
// this.root is the root node of the Tree
this.root = new Node(rowCount);
this.createAllChildren(this.root, rowCount-1, childrenCount);
}
public void dfsRecursive() {
this.dfsRecursive(this.root);
}
private void dfsRecursive(Node node) {
System.out.print(node.id + " ");
for (Node n : node.children) {
dfsRecursive(n);
}
}
public void dfsRecursivePostOrder() {
this.dfsRecursivePostOrder(this.root);
}
private void dfsRecursivePostOrder(Node node) {
for (Node n : node.children) {
dfsRecursivePostOrder(n);
}
// Here we are doing something ...
System.out.print(node.id + " ");
}
public void dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary() {
dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(this.root);
}
private void dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(Node node) {
switch (node.children.size()) {
case 2:
dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(node.children.get(0));
System.out.print(node.id + " ");
dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(node.children.get(1));
break;
case 1:
dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(node.children.get(0));
System.out.print(node.id + " ");
break;
case 0:
System.out.print(node.id + " ");
break;
default:
System.err.println("Not a binary tree at dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary()!");
}
}
public void dfsStack() {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
stack.push(this.root);
Node tmp;
while (stack.size() != 0) {
System.out.print(stack.peek().id + " ");
tmp = stack.pop();
for (Node c : tmp.children) {
stack.push(c);
}
}
}
public void bfsQueue() {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
queue.add(this.root);
while (queue.size() != 0) {
System.out.print(queue.peek().id + " ");
Node temp = queue.poll(); // return null if the queue is empty
if (temp != null) {
for (Node c : temp.children) {
queue.add(c);
}
}
}
}
private void createAllChildren(Node node, int rowCount, int childrenCount) {
if (rowCount < 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < childrenCount; i++) {
node.children.add(new Node(rowCount));
createAllChildren(node.children.get(i), rowCount - 1, childrenCount);
}
}
private class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
public ArrayList<Node> children;
public int id;
public Node(int id) {
this.children = new ArrayList<Node>();
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node other) {
// Need to implement Comparable<Node> and override this
// method because of the method BFSQueue() which uses Queues
// and must know how to check if two nodes are the same or not
return Integer.compare(this.id, other.id);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tree tree = new Tree(2, 3);
System.out.println("[#]\nRecursive DFS:");
tree.dfsRecursive();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("[#]\nRecursive Postorder DFS:");
tree.dfsRecursivePostOrder();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("[#]\nStack-based DFS:");
tree.dfsStack();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("[#]\nQueue-based BFS:");
tree.bfsQueue();
System.out.println();
// Uncommenting the following 2 lines will result in an exception thrown because at least one Node of the Tree has more than 2 children and therefor a DFSRecursiveInorderBinary doesn't work.
//System.out.println("Using in-order binary recursive DFS : (fail)");
//tree.dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary();
tree = new Tree(3, 2);
System.out.println("[#]\nRecursive Inorder DFS for Binary Tree:");
tree.dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary();
System.out.println();
}
}
function createTree(rows, children) {
if (rows === 0) {
return { id: rows, children: [] };
}
return {
id: rows,
children: [...Array(children).keys()].map(() => createTree(rows - 1, children))
};
}
function dfsPreorder(tree) {
if (!tree) {
return;
}
process.stdout.write(tree.id + " ");
tree.children.forEach(dfsPreorder);
}
function dfsPostorder(tree) {
if (!tree) {
return;
}
tree.children.forEach(dfsPostorder);
process.stdout.write(tree.id + " ");
}
function dfsInorder(tree) {
if (!tree) {
return;
}
switch (tree.children.length) {
case 2:
dfsInorder(tree.children[0]);
console.log(tree.id);
dfsInorder(tree.children[1]);
break;
case 1:
dfsInorder(tree.children[0]);
console.log(tree.id);
break;
case 0:
console.log(tree.id);
break;
default:
throw new Error("Postorder traversal is only valid for binary trees");
}
}
function dfsIterative(tree) {
const stack = [tree];
while (stack.length > 0) {
const current = stack.pop();
process.stdout.write(current.id + " ");
stack.push(...current.children);
}
}
function bfs(tree) {
const queue = [tree];
while (queue.length > 0) {
const current = queue.shift();
process.stdout.write(current.id + " ");
queue.push(...current.children);
}
}
const root = createTree(2, 3);
console.log("[#]\nRecursive DFS:");
dfsPreorder(root);
console.log();
console.log("[#]\nRecursive Postorder DFS:");
dfsPostorder(root);
console.log();
console.log("[#]\nStack-based DFS:");
dfsIterative(root);
console.log();
console.log("[#]\nQueue-based BFS:");
bfs(root);
console.log();
const root_binary = createTree(3, 2);
console.log("[#]\nRecursive Inorder DFS for Binary Tree:");
dfsInorder(root_binary);
console.log();
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.data = None
self.children = []
def create_tree(node, num_row, num_child):
node.data = num_row
if num_row > 0:
for i in range(num_child):
child = create_tree(Node(), num_row-1, num_child)
node.children.append(child)
return node
def dfs_recursive(node):
if node.data != None:
print(node.data, end=' ')
for child in node.children:
dfs_recursive(child)
def dfs_recursive_postorder(node):
for child in node.children:
dfs_recursive_postorder(child)
if node.data != None:
print(node.data, end=' ')
# This assumes only 2 children, but accounts for other possibilities
def dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(node):
if len(node.children) == 2:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(node.children[0])
print(node.data, end=' ')
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(node.children[1])
elif len(node.children) == 1:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(node.children[0])
print(node.data, end=' ')
elif len(node.children) == 0:
print(node.data, end=' ')
else:
print("Not a binary tree!")
def dfs_stack(node):
stack = [node]
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
stack.extend(node.children)
print(node.data, end=' ')
def bfs_queue(node):
queue = [node]
while queue:
node = queue.pop(0)
queue.extend(node.children)
print(node.data)
def main():
tree = create_tree(Node(), 2, 3)
print("[#]\nRecursive DFS:")
dfs_recursive(tree)
print()
print("[#]\nRecursive Postorder DFS:")
dfs_recursive_postorder(tree)
print()
print("[#]\nStack-based DFS:")
dfs_stack(tree)
print()
print("[#]\nQueue-based BFS:")
bfs_queue(tree)
print()
binary_tree = create_tree(Node(), 3, 2)
print("[#]\nRecursive Inorder DFS for Binary Tree:")
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(binary_tree)
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
The code snippets were taken from this Scratch project
use std::collections::VecDeque;
#[derive(Debug)]
struct Node {
children: Vec<Node>,
value: u64,
}
fn dfs_recursive(n: &Node) {
print!("{} ", n.value);
for child in &n.children {
dfs_recursive(child);
}
}
fn dfs_recursive_postorder(n: &Node) {
for child in &n.children {
dfs_recursive_postorder(child);
}
print!("{} ", n.value);
}
fn dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(n: &Node) {
match &n.children[..] {
[left, right] => {
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(left);
print!("{} ", n.value);
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(right);
}
[left] => {
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(left);
print!("{} ", n.value);
}
[] => print!("{} ", n.value),
_ => print!("This is not a binary tree. "),
}
}
fn dfs_stack(n: &Node) {
let mut stack = vec![n];
while let Some(current) = stack.pop() {
print!("{} ", current.value);
stack.extend(¤t.children);
}
}
fn bfs_queue(n: &Node) {
let mut queue = VecDeque::new();
queue.push_back(n);
while let Some(current) = queue.pop_front() {
print!("{} ", current.value);
queue.extend(¤t.children);
}
}
fn create_tree(num_row: u64, num_child: u64) -> Node {
if num_row == 0 {
return Node {
children: vec![],
value: 0,
};
}
let children = (0..num_child)
.map(|_| create_tree(num_row - 1, num_child))
.collect();
Node {
children,
value: num_row,
}
}
fn main() {
let root = create_tree(2, 3);
println!("[#]\nRecursive DFS:");
dfs_recursive(&root);
println!();
println!("[#]\nRecursive Postorder DFS:");
dfs_recursive_postorder(&root);
println!();
println!("[#]\nStack-based DFS:");
dfs_stack(&root);
println!();
println!("[#]\nQueue-based BFS:");
bfs_queue(&root);
println!();
println!("[#]\nRecursive Inorder DFS for Binary Tree:");
let root_binary = create_tree(3, 2);
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(&root_binary);
println!();
}
data Tree a = Node
{ node :: a,
forest :: [Tree a]
}
deriving (Show)
dfs :: Tree a -> [a]
dfs (Node x ts) = x : concatMap dfs ts
dfsPostOrder :: Tree a -> [a]
dfsPostOrder (Node x ts) = concatMap dfsPostOrder ts ++ [x]
dfsInOrder :: Tree a -> [a] -- For binary trees only
dfsInOrder (Node x []) = [x]
dfsInOrder (Node x [l]) = dfsInOrder l ++ [x] -- Single branch assumed to be left
dfsInOrder (Node x [l, r]) = dfsInOrder l ++ [x] ++ dfsInOrder r
dfsInOrder _ = error "Not a binary tree"
dfsStack :: Tree a -> [a]
dfsStack t = go [t]
where
go [] = []
go ((Node x ts) : stack) = x : go (ts ++ stack)
bfs :: Tree a -> [a]
bfs (Node x ts) = x : go ts
where
go [] = []
go ts = map node ts ++ go (concatMap forest ts)
createTree :: Int -> Int -> Tree Int
createTree 0 _ = Node 0 []
createTree numRow numChild = Node numRow children
where
children = map (createTree (numRow - 1)) $ replicate numChild numChild
main = do
let testTree = createTree 2 3
showNodes = unwords . map show
putStrLn "[#]\nRecursive DFS:"
putStrLn $ showNodes $ dfs testTree
putStrLn "[#]\nRecursive Postorder DFS:"
putStrLn $ showNodes $ dfsPostOrder testTree
putStrLn "[#]\nStack-based DFS:"
putStrLn $ showNodes $ dfsStack testTree
putStrLn "[#]\nQueue-based BFS:"
putStrLn $ showNodes $ bfs testTree
putStrLn "[#]\nRecursive Inorder DFS for Binary Tree:"
putStrLn $ showNodes $ dfsInOrder $ createTree 3 2
class Node {
var value: Int
var children: [Node]?
init(value: Int, children: [Node]) {
self.value = value
self.children = children
}
}
func createTree(numRows: Int, numChildren: Int) -> Node {
let node = Node(value: numRows, children: [])
if numRows > 0 {
for _ in 1...numChildren {
let child = createTree(numRows: numRows-1, numChildren: numChildren)
node.children?.append(child)
}
}
return node
}
func dfsRecursive(node: Node) {
print(node.value, terminator:" ")
for child in node.children! {
dfsRecursive(node: child)
}
}
func dfsRecursivePostOrder(node: Node) {
for child in node.children! {
dfsRecursivePostOrder(node: child)
}
print(node.value, terminator:" ")
}
func dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(node: Node) {
if node.children?.count == 2 {
dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(node: node.children![0])
print(node.value, terminator:" ")
dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(node: node.children![1])
} else if node.children?.count == 1 {
dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(node: node.children![0])
print(node.value, terminator:" ")
} else if node.children?.count == 0 {
print(node.value, terminator:" ")
} else {
print("Not a binary tree!")
}
}
func dfsStack(node: Node) {
var stack = [node]
var temp: Node
while stack.count > 0 {
temp = stack.popLast()!
print(temp.value, terminator:" ")
for child in temp.children! {
stack.append(child)
}
}
}
func bfsQueue(node: Node) {
var queue = [node]
var temp: Node
while queue.count > 0 {
temp = queue.remove(at: 0)
print(temp.value, terminator:" ")
for child in temp.children! {
queue.append(child)
}
}
}
func main() {
let root = createTree(numRows: 2, numChildren: 3)
print("[#]\nRecursive DFS:")
dfsRecursive(node: root)
print()
print("[#]\nRecursive Postorder DFS:")
dfsRecursivePostOrder(node: root)
print()
print("[#]\nStack-based DFS:")
dfsStack(node: root)
print()
print("[#]\nQueue-based BFS:")
bfsQueue(node: root)
print()
let rootBinary = createTree(numRows: 3, numChildren: 2)
print("[#]\nRecursive Inorder DFS for Binary Tree:")
dfsRecursiveInOrderBinary(node: rootBinary)
print()
}
main()
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
class Tree implements JsonSerializable
{
private $id;
private $children = [];
public function __construct(int $id, array $children = [])
{
$this->id = $id;
$this->children = $children;
}
public function getId(): int
{
return $this->id;
}
public function getChildren(): array
{
return $this->children;
}
public function addChild(Tree $child): void
{
$this->children[] = $child;
}
public function jsonSerialize(): array
{
return [
'id' => $this->id,
'children' => $this->children,
];
}
}
class TreeTraversal
{
public static function DFSRecursive(Tree $tree): void
{
echo $tree->getId() . ' ';
foreach ($tree->getChildren() as $child) {
static::DFSRecursive($child);
}
}
public static function DFSRecursivePostorder(Tree $tree): void
{
foreach ($tree->getChildren() as $child) {
static::DFSRecursivePostorder($child);
}
echo $tree->getId() . ' ';
}
public static function DFSRecursiveInorderBinary(Tree $tree): void
{
switch (count($tree->getChildren())) {
case 2:
static::DFSRecursiveInorderBinary($tree->getChildren()[0]);
echo $tree->getId() . ' ';
static::DFSRecursiveInorderBinary($tree->getChildren()[1]);
break;
case 1:
static::DFSRecursiveInorderBinary($tree->getChildren()[0]);
echo $tree->getId() . ' ';
break;
case 0:
echo $tree->getId() . ' ';
break;
default:
throw new InvalidArgumentException('Not a binary tree!');
break;
}
}
public static function DFSStack(Tree $tree): void
{
$stack = [$tree];
$temp = null;
while (null !== ($temp = array_pop($stack))) {
echo $temp->getId() . ' ';
foreach ($temp->getChildren() as $child) {
$stack[] = $child;
}
}
}
public static function DFSQueue(Tree $tree): void
{
$stack = [$tree];
$temp = null;
while (null !== ($temp = array_shift($stack))) {
echo $temp->getId() . ' ';
foreach ($temp->getChildren() as $child) {
$stack[] = $child;
}
}
}
}
function generate_tree(int $numOfRows, int $numOfChildren): Tree
{
$node = new Tree($numOfRows);
if ($numOfRows > 0) {
for ($i = 0; $i < $numOfChildren; $i++) {
$child = generate_tree($numOfRows - 1, $numOfChildren);
$node->addChild($child);
}
}
return $node;
}
$node = generate_tree(2, 3);
echo '[#]' . PHP_EOL . 'Recursive DFS:' . PHP_EOL;
TreeTraversal::DFSRecursive($node);
echo PHP_EOL;
echo '[#]' . PHP_EOL . 'Recursive Postorder DFS:' . PHP_EOL;
TreeTraversal::DFSRecursivePostorder($node);
echo PHP_EOL;
echo '[#]' . PHP_EOL . 'Stack-based DFS:' . PHP_EOL;
TreeTraversal::DFSStack($node);
echo PHP_EOL;
echo '[#]' . PHP_EOL . 'Queue-based BFS:' . PHP_EOL;
TreeTraversal::DFSQueue($node);
echo PHP_EOL;
// If you want to try to run binary order on a non-binary tree,
// comment out the generation of the new tree below.
// If you do that, an exception will be thrown
$node = generate_tree(3, 2);
echo '[#]' . PHP_EOL . 'Recursive Inorder DFS for Binary Tree:' . PHP_EOL;
TreeTraversal::DFSRecursiveInorderBinary($node);
echo PHP_EOL;
class Node
property id, children
def initialize(@id : Int32, @children : Array(Node))
end
end
def dfs_recursive(node)
print "#{node.id} "
node.children.each{ |child| dfs_recursive child }
end
def dfs_recursive_postorder(node)
node.children.each{ |child| dfs_recursive_postorder child }
print "#{node.id} "
end
def dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(node)
case node.children.size
when 2
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree node.children[0]
print "#{node.id} "
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree node.children[1]
when 1
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree node.children[0]
print "#{node.id} "
when 0
print "#{node.id} "
else
print "Not a binary tree!"
end
end
def dfs_stack(node)
stack = [node]
until stack.empty?
temp = stack.pop
print "#{temp.id} "
temp.children.each{ |child| stack.push child }
end
end
def bfs_queue(node)
queue = Deque.new [node]
until queue.empty?
temp = queue.shift
print "#{temp.id} "
temp.children.each{ |child| queue.push child }
end
end
def create_tree(levels, num_childs)
children = [] of Node
unless levels == 0
num_childs.times{children.push create_tree levels-1, num_childs }
end
Node.new(levels, children)
end
def main
root = create_tree levels: 2, num_childs: 3
puts "[#]\nRecursive DFS:"
dfs_recursive root
puts
puts "[#]\nRecursive Postorder DFS:"
dfs_recursive_postorder root
puts
puts "[#]\nStack-based DFS:"
dfs_stack root
puts
puts "[#]\nQueue-based BFS:"
bfs_queue root
puts
root_bin = create_tree levels: 3, num_childs: 2
puts "[#]\nRecursive Inorder DFS for Binary Tree:"
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree root_bin
puts
end
main
Object subclass: #Node
instanceVariableNames: 'children data'
classVariableNames: ''
package: ''
Node>>children
"Children getter."
^ children
Node>>children: newChildren
"Children setter."
children := newChildren.
Node>>data
"Data getter"
^ data
Node>>data: newData
"Data setter"
data := newData.
Node>>dfsRecursive
"Recursive depth first search."
Transcript show: data; cr.
children collect: [ :child | child dfsRecursive ]
Node>>dfsRecursivePostOrder
"Recursive depth first search (post-order)."
children collect: [ :child | (child dfsRecursivePostOrder)].
Transcript show: data; cr.
Node>>dfsInOrderBinaryTree
"Recursive depth first search on a binary tree in order."
children size > 2 ifTrue: [
Transcript show: 'This is not a binary tree!'; cr.
^self.
].
children size = 2 ifTrue: [
(children at: 1) dfsInOrderBinaryTree: value.
].
Transcript show: data; cr.
children size >= 1 ifTrue: [
(children at: 0) dfsInOrderBinaryTree: value.
].
^self.
Node>>dfsStack
"Depth-first search with a stack."
| stack top |
stack := Stack new.
stack push: self.
[stack size > 0] whileTrue: [
top := stack pop.
Transcript show: (top data); cr.
top children reverseDo: [ :child |
stack push: child.
].
].
Node>>bfs
"A breadth-first tree search using queues."
| queue current |
queue := LinkedList with: self.
[ queue size > 0 ] whileTrue: [
current := queue first.
queue removeFirst.
Transcript show: (current data); cr.
current children collect: [ :child |
queue addLast: child
].
].
| test |
test := Node new: 1 children: { Node new: 2.
Node new: 3 children: { Node new: 4.
Node new: 5. } }.
test dfsRecursive.
test dfsRecursivePostorder.
test dfsInOrderBinaryTree.
test dfsStack.
test bfs.
package main
import "fmt"
type node struct {
id int
children []*node
}
func dfsRecursive(n *node) {
fmt.Printf("%d ", n.id)
for _, child := range n.children {
dfsRecursive(child)
}
}
func dfsRecursivePostorder(n *node) {
for _, child := range n.children {
dfsRecursivePostorder(child)
}
fmt.Printf("%d ", n.id)
}
func dfsRecursiveInorderBtree(n *node) {
switch len(n.children) {
case 2:
dfsRecursiveInorderBtree(n.children[0])
fmt.Printf("%d ", n.id)
dfsRecursiveInorderBtree(n.children[1])
case 1:
dfsRecursiveInorderBtree(n.children[0])
fmt.Printf("%d ", n.id)
case 0:
fmt.Printf("%d ", n.id)
default:
fmt.Println("This is not a binary tree")
}
}
func dfsStack(n *node) {
stack := []*node{n}
for len(stack) > 0 {
cur := stack[0]
stack = stack[1:]
fmt.Printf("%d ", cur.id)
stack = append(cur.children, stack...)
}
}
func bfsQueue(n *node) {
queue := []*node{n}
for len(queue) > 0 {
cur := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
fmt.Printf("%d ", cur.id)
queue = append(queue, cur.children...)
}
}
func createTree(numRow, numChild int) *node {
if numRow == 0 {
return &node{id: 0}
}
cur := new(node)
cur.id = numRow
for x := 0; x < numChild; x++ {
cur.children = append(cur.children, createTree(numRow-1, numChild))
}
return cur
}
func main() {
root := createTree(2, 3)
binTree := createTree(3, 2)
fmt.Println("[#]\nRecursive DFS:")
dfsRecursive(root)
fmt.Println()
fmt.Println("[#]\nRecursive Postorder DFS:")
dfsRecursivePostorder(root)
fmt.Println()
fmt.Println("[#]\nStack-based DFS:")
dfsStack(root)
fmt.Println()
fmt.Println("[#]\nQueue-based BFS:")
bfsQueue(root)
fmt.Println()
fmt.Println("[#]\nRecursive Inorder DFS for Binary Tree:")
dfsRecursiveInorderBtree(binTree)
fmt.Println()
}
.intel_syntax noprefix
# System V calling convention cheatsheet
# Params: rdi, rsi, rdx, rcx, r8, r9, xmm0-7
# Return: rax (int 64 bits), rax:rdx (int 128 bits), xmm0 (float)
# Callee cleanup: rbx, rbp, r12-15
# Scratch: rax, rdi, rsi, rdx, rcx, r8, r9, r10, r11
.section .rodata
not_bt: .string "This is not a binary tree.\n"
fmt_tree: .string "%d \n"
.equ stack_size, 16
.equ stack_array, 0
.equ stack_top, 8
.equ stack_cap, 12
.equ queue_size, 20
.equ queue_array, 0
.equ queue_front, 8
.equ queue_back, 12
.equ queue_cap, 16
.equ tree_children, 0
.equ tree_num_children, 8
.equ tree_value, 12
.equ tree_size, 16
.section .text
.global main
.extern printf, malloc, free, memcpy
# rdi - stack ptr
get_stack:
push r12
mov r12, rdi
mov rdi, 32 # Creating a 32 byte array
call malloc
mov QWORD PTR [r12], rax # Saving the data into the stack
mov DWORD PTR [r12 + 8], 0
mov DWORD PTR [r12 + 12], 32
pop r12
ret
# rdi - stack ptr
# rsi - element ptr
stack_push:
push r12
push r13
push r14
mov r12, rdi # Saving the variables
mov r13, rsi
mov r14d, DWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
mov esi, DWORD PTR [r12 + 12]
cmp rsi, r14 # Check if top is equal to capacity
jne stack_push_append
shl rsi, 1 # Calculate new capacity in bytes
mov DWORD PTR [r12 + 12], esi # Saving new capcaity
mov rdi, [r12]
call realloc # Making the array bigger
mov QWORD PTR [r12], rax
stack_push_append:
add r14, 8
mov rax, QWORD PTR [r12]
lea rax, [rax + r14]
mov QWORD PTR [rax], r13 # Saving element and new top
mov DWORD PTR [r12 + 8], r14d
pop r14
pop r13
pop r12
ret
# rdi - stack ptr
# RET rax - element ptr
stack_pop:
push r12
mov r12d, DWORD PTR [rdi + 8] # Get top
test r12, r12 # Check if top is zero
jne stack_pop_element
xor rax, rax # Return 0
jmp stack_pop_return
stack_pop_element:
mov rax, [rdi]
lea rax, [rax + r12] # Get the element
mov rax, QWORD PTR [rax]
sub r12, 8 # Subtract 1 from top and save it
mov DWORD PTR [rdi + 8], r12d
stack_pop_return:
pop r12
ret
# rdi - stack ptr
free_stack:
mov rdi, QWORD PTR [rdi]
call free # Free stack array
ret
# rdi - queue ptr
get_queue:
push r12
mov r12, rdi
mov rdi, 32 # Create a 32 byte array
call malloc
mov QWORD PTR [r12], rax # Saving data to the queue pointer
mov QWORD PTR [r12 + 8], 0
mov DWORD PTR [r12 + 16], 32
pop r12
ret
# rdi - queue ptr
queue_resize:
push r12
push r13
push r14
mov r12, rdi
mov edi, DWORD PTR [r12 + 16] # Get new capacity and create new array
shl rdi, 1
call malloc
mov r13, rax
mov r14, QWORD PTR[r12]
mov rdi, r13 # Copy data from front to capacity
mov eax, DWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
lea rsi, [r14 + rax]
mov edx, DWORD PTR [r12 + 16]
sub edx, DWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
call memcpy
mov eax, DWORD PTR [r12 + 16] # Copy data from start of array to front
sub eax, DWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
lea rdi, [r13 + rax]
mov rsi, r14
mov edx, DWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
call memcpy
mov rdi, r14 # New array has front at 0 and back at the old capacity
call free # So free the old array then save the new queue
mov QWORD PTR [r12], r13
mov eax, DWORD PTR [r12 + 16]
sub rax, 8
mov DWORD PTR [r12 + 12], eax
mov DWORD PTR [r12 + 8], 0
mov eax, DWORD PTR [r12 + 16]
shl rax, 1
mov DWORD PTR [r12 + 16], eax
pop r14
pop r13
pop r12
ret
# rdi - queue ptr
# rsi - element
enqueue:
push r12
push r13
push r14
push r15
mov r12, rdi # Saving parameters
mov r13, rsi
mov r14d, DWORD PTR [rdi + 8]
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rdi + 12]# Calculating new back
add eax, 8
mov edi, DWORD PTR [r12 + 16]
cdq
idiv edi
cmp rdx, r14 # Check if front and new back are equal
jne enqueue_append
mov rdi, r12 # If so resize the queue
call queue_resize
enqueue_append:
mov r14, QWORD PTR [r12] # Saving the element
mov r15d, DWORD PTR [r12 + 12]
lea r14, [r14 + r15]
mov QWORD PTR [r14], r13
mov r14d, DWORD PTR [r12 + 16]# Calculating new back and then saving it
add r15, 8
mov rax, r15
cdq
idiv r14d
mov DWORD PTR [r12 + 12], edx
pop r15
pop r14
pop r13
pop r12
ret
# rdi - queue ptr
# RET rax - element
dequeue:
push r12
push r13
mov r12d, DWORD PTR [rdi + 8] # Check if queue is empty
mov r13d, DWORD PTR [rdi + 12]
xor rax, rax
cmp r12, r13
je dequeue_return # if empty return null
mov r12, QWORD PTR [rdi] # else return element pointer
mov r13d, DWORD PTR [rdi + 8]
lea r13, [r12 + r13]
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rdi + 8]
add eax, 8
mov r12d, DWORD PTR [rdi + 16] # Calculate new front
cdq
idiv r12d
mov DWORD PTR [rdi + 8], edx # Save new front
mov rax, QWORD PTR [r13]
dequeue_return:
pop r13
pop r12
ret
# rdi - queue ptr
free_queue:
mov rdi, QWORD PTR [rdi] # Free queue array
call free
ret
# rdi - levels
# rsi - children_size
# RET rax:rdx - the tree - children|value|children_size
create_tree:
push rbx
push r12
push r13
push r14
push r15
mov r12, rdi
mov r13, rsi
test rdi, rdi
jz create_tree_leaf
mov r14, rsi # We'll allocate sizeof(tree) * children_size bytes of memory
shl r14, 4 # save the size calculation to a callee-saved register so we can reuse it after the malloc
mov rdi, r14
call malloc
mov r15, rax # Save the children address twice, once for the return value, once for the loop variable
mov rbx, rax
lea r14, [rax + r14] # Calculate the address of the element after last of the children array
create_tree_children:
cmp rbx, r14
je create_tree_return
lea rdi, [r12 - 1] # levels - 1
mov rsi, r13
call create_tree
mov QWORD PTR [rbx], rax # Save the created tree to memory
mov QWORD PTR [rbx + 8], rdx # The offset of children_size, writing out explicitly would've made the line way too long
add rbx, tree_size
jmp create_tree_children
create_tree_leaf:
mov r15, 0
xor r13, r13 # Leaves won't have any children
create_tree_return:
mov rax, r15 # The children pointer will be in r15
mov rdx, r12
shl rdx, 32 # The tree's value will be the current "levels"
shl r13, 4
or rdx, r13 # Generate the return value by moving the value to the upper 32 bits
pop r15
pop r14
pop r13
pop r12
pop rbx
ret
# rdi - children ptr
# rsi - children size
free_tree:
push r12
push r13
push r14
push r15
test rdi, rdi # Make sure the pointer is non-zero
jz free_tree_return
mov r12, rdi # Saving array
lea r13, [r12 + rsi] # Get start and end of the array
mov r14, r12
free_tree_free_kid:
cmp r14, r13 # Loop thought the array and free all children
je free_tree_free_array
mov rdi, QWORD PTR [r14]
mov esi, DWORD PTR [r14 + 8]
call free_tree
add r14, tree_size
jmp free_tree_free_kid
free_tree_free_array:
mov rdi, r12 # Free the array
call free
free_tree_return:
pop r15
pop r14
pop r13
pop r12
ret
# rdi - children ptr
# rsi - value|children_size
dfs_recursive:
push r12
push r13
mov r12, rdi
mov r13, rsi
mov rdi, OFFSET fmt_tree # Handle the current node
shr rsi, 32 # The tree value is in the upper 32 bits
xor rax, rax
call printf
mov r13d, r13d # Zero out the top 32 bits
add r13, r12 # Pointer pointing after the last element of the children array
dfs_recursive_children:
cmp r12, r13 # If we reached the end, return
je dfs_recursive_return
mov rdi, QWORD PTR [r12]
mov rsi, QWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
call dfs_recursive
add r12, tree_size
jmp dfs_recursive_children
dfs_recursive_return:
pop r13
pop r12
ret
# rdi - children ptr
# rsi - value|children_size
dfs_recursive_postorder:
push r12
push r13
push r14
mov r12, rdi
mov r13, rsi
mov r14, rsi
mov r13d, r13d # Zero out the top 32 bits
add r13, r12 # Pointer pointing after the last element of the children array
dfs_recursive_po_children:
cmp r12, r13 # If we reached the end, return
je dfs_recursive_po_return
mov rdi, QWORD PTR [r12]
mov rsi, QWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
call dfs_recursive_postorder
add r12, tree_size
jmp dfs_recursive_po_children
dfs_recursive_po_return:
mov rdi, OFFSET fmt_tree # Handle the current node
mov rsi, r14
shr rsi, 32 # The tree value is in the upper 32 bits
xor rax, rax
call printf
pop r14
pop r13
pop r12
ret
# rdi - children ptr
# rsi - value|children_size
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree:
push r12
push r13
mov r12, rdi
mov r13, rsi
mov rax, rsi
mov eax, eax
cmp rax, 0 # Check what type of tree it is.
je dfs_recursive_bt_size0
cmp rax, 16
je dfs_recursive_bt_size1
cmp rax, 32
je dfs_recursive_bt_size2
mov rdi, OFFSET not_bt # If the tree is not binary then print a warning
xor rax, rax
call printf
jmp dfs_recursive_bt_return
dfs_recursive_bt_size0:
mov rdi, OFFSET fmt_tree # If the node is a leaf then print its id
shr rsi, 32
xor rax, rax
call printf
jmp dfs_recursive_bt_return
dfs_recursive_bt_size1:
mov rdi, QWORD PTR [r12] # If the node has 1 child then call the function and print the id
mov rsi, QWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
call dfs_recursive_inorder_btree
mov rdi, OFFSET fmt_tree
mov rsi, r13
shr rsi, 32
xor rax, rax
call printf
jmp dfs_recursive_bt_return
dfs_recursive_bt_size2:
mov rdi, QWORD PTR [r12] # Same as above just print id inbetween the calls
mov rsi, QWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
call dfs_recursive_inorder_btree
mov rdi, OFFSET fmt_tree
mov rsi, r13
shr rsi, 32
xor rax, rax
call printf
mov rdi, QWORD PTR [r12 + 16]
mov rsi, QWORD PTR [r12 + 24]
call dfs_recursive_inorder_btree
dfs_recursive_bt_return:
pop r13
pop r12
ret
# rdi - children ptr
# rsi - value|children_size
dfs_stack:
push r12
push r13
push r14
sub rsp, 16 # Create stack
mov r12, rsp
push rsi # Save node to use as pointer
push rdi
mov rdi, r12
call get_stack # Init stack
mov rdi, r12
mov rsi, rsp
call stack_push # Push node
mov rdi, r12 # Pop stack
call stack_pop
dfs_stack_loop:
test rax, rax # Test if stack is empty
jz dfs_stack_return
mov r13, rax
mov rdi, OFFSET fmt_tree # Print id
mov esi, DWORD PTR [r13 + 12]
xor rax, rax
call printf
mov eax, DWORD PTR [r13 + 8] # Get start and end of array
mov r13, QWORD PTR [r13]
lea r14, [r13 + rax]
dfs_stack_push_child:
cmp r13, r14 # Check if the pointers are the same
je dfs_stack_end_push
mov rdi, r12 # Push node into the stack
mov rsi, r13
call stack_push
add r13, tree_size
jmp dfs_stack_push_child
dfs_stack_end_push:
mov rdi, r12 # Pop stack
call stack_pop
jmp dfs_stack_loop
dfs_stack_return:
mov rdi, r12 # Free stack
call free_stack
add rsp, 32
pop r14
pop r13
pop r12
ret
# rdi - children ptr
# rsi - value|children_size
bfs_queue:
push r12
push r13
push r14
sub rsp, 20 # Create queue
mov r12, rsp
push rsi # Save node to use as pointer
push rdi
mov rdi, r12
call get_queue # Init queue
mov rdi, r12
mov rsi, rsp
call enqueue # enqueue node
mov eax, DWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
mov edi, DWORD PTR [r12 + 12]
bfs_queue_loop:
cmp eax, edi
je bfs_queue_return
mov rdi, r12 # dequeue
call dequeue
test rax, rax # Test if queue is empty
jz bfs_queue_return
mov r13, rax
mov rdi, OFFSET fmt_tree # Print id
mov esi, DWORD PTR [r13 + 12]
xor rax, rax
call printf
mov eax, DWORD PTR [r13 + 8] # Get start and end of array
mov r13, QWORD PTR [r13]
lea r14, [r13 + rax]
bfs_queue_push_child:
cmp r13, r14 # Check if the pointers are the same
je bfs_queue_end_push
mov rdi, r12 # enqueue node
mov rsi, r13
call enqueue
add r13, tree_size
jmp bfs_queue_push_child
bfs_queue_end_push:
mov eax, DWORD PTR [r12 + 8]
mov edi, DWORD PTR [r12 + 12]
jmp bfs_queue_loop
bfs_queue_return:
mov rdi, r12 # Free queue
call free_queue
add rsp, 36
pop r14
pop r13
pop r12
ret
main:
push r12
push r13
mov rdi, 3
mov rsi, 3
call create_tree
mov r12, rax
mov r13, rdx
mov rdi, rax
mov rsi, rdx
call bfs_queue
mov rdi, r12
mov rsi, r13
mov esi, esi
call free_tree
pop r13
pop r12
ret
🦃 ⏹ 🍇
🔘 ⏫
❗️ 🔡 ➡️ 🔡 🍇
↪️ 🐕 🙌 🆕⏹⏫❗️ 🍇
↩️ 🔤The given tree is not binary!🔤
🍉
↩️ 🔤🔤
🍉
🍉
🐇 🌲 🍇
🖍🆕 id 🔢
🖍🆕 children 🍨🐚🌲🍆
🆕 depth_count 🔢 children_count 🔢 🍇
1 ➡️ 🖍id
🍨🍆 ➡️ 🖍children
🌌🐕 depth_count children_count❗️
🍉
🔐 🆕 ⭐️ given_id 🔢 depth_count 🔢 children_count 🔢 🍇
given_id ➡️ 🖍id
🍨🍆 ➡️ 🖍children
🌌🐕 depth_count children_count❗️
🍉
❗️ 🆔 ➡️ 🔢 🍇
↩️ id
🍉
❗️ 🧒 ➡️ 🍨🐚🌲🍆 🍇
↩️ children
🍉
📗 Depth-First Search Recursive pre-order 📗
❗️ 🌀 🍇
😀 🔡 id 10❗️❗️
🔂 child children 🍇
🌀 child❗️
🍉
🍉
📗 Depth-First Search Recursive post-order 📗
❗️ 🍥 🍇
🔂 child children 🍇
🍥 child❗️
🍉
😀 🔡 id 10❗️❗️
🍉
📗
Depth-First Search Recursive Inorder Binary
This assumes only 2 children.
📗
❗️ 🍭 ➡️ 🍬⏹ 🍇
↪️ 🐔 children❗️ ▶️ 2 🍇
↩️ 🆕⏹⏫❗️
🍉
↪️ 🐔 children❗️ ▶️ 0 🍇
🍭🐽 children 0❗️❗️
😀 🔡 id 10❗️❗️
🍭🐽 children 1❗️❗️
🍉
🙅 🍇
😀 🔡 id 10❗️❗️
🍉
↩️ 🤷♀️
🍉
📗 Depth-First Search Stack 📗
❗️ 🥞 🍇
🍨 🐕 🍆 ➡️ stack
🔁 ❎ 🐔 stack❗️ 🙌 0❗️ 🍇
🐽 stack 🐔 stack❗️ ➖ 1❗️ ➡️ temp
🐨 stack 🐔 stack❗️ ➖ 1❗️
😀 🔡 🆔 temp❗️ 10❗️❗️
🧒 temp❗️ ➡️ temp_children
🔂 child temp_children 🍇
🐻 stack child❗️
🍉
🍉
🍉
📗 Breadth-First Search Queue 📗
❗️ 🏢 🍇
🍨 🐕 🍆 ➡️ queue
🔁 ❎ 🐔 queue❗️ 🙌 0❗️ 🍇
🐽 queue 0❗️ ➡️ temp
🐨 queue 0❗️
😀 🔡 🆔 temp❗️ 10❗️❗️
🧒 temp❗️ ➡️ temp_children
🔂 child temp_children 🍇
🐻 queue child❗️
🍉
🍉
🍉
🔐 ❗️ 🌌 depth_count 🔢 children_count 🔢 🍇
↪️ ❎ depth_count ◀️🙌 1❗️ 🍇
🔂 i 🆕⏩⏩ 0 children_count❗️ 🍇
🐻 children 🆕🌲⭐️ 🤜id ✖️ 10 ➕ i ➕ 1🤛 🤜depth_count ➖ 1🤛 children_count❗️❗️
🍉
🍉
🍉
🍉
🏁 🍇
🆕🌲🆕 3 3❗️ ➡️ tree
😀 🔤Tree Traversal🔤️❗️
😀 🔤🌀 - Depth-First Search Recursive pre-order🔤❗️
🌀tree❗️
😀 🔤🍥 - Depth-First Search Recursive post-order🔤❗️
🍥tree❗️
😀 🔤🥞 - Depth-First Search Stack🔤❗️
🥞tree❗️
😀 🔤🏢 - Breadth-First Search Queue🔤❗️
🏢tree❗️
😀 🔤🍭 - Depth-First Search Recursive Inorder Binary - Error🔤❗️
💭 Calling the Depth-First Search Recursive Inorder Binary method here does
💭 result in an error, since "tree" is not a binary tree.
️↪️ 🍭tree❗️ ➡️ return 🍇
😀 🔡return❗❗️️
🍉
🆕🌲🆕 3 2❗️ ➡️ binary_tree
😀 🔤🍭 - Depth-First Search Recursive Inorder Binary🔤❗️
️↪️ 🍭binary_tree❗️ ➡️ return 🍇
😀 🔡return❗❗️️
🍉
🍉
;;;; Tree traversal in Common Lisp
(defstruct node data children)
(defun dfs-recursive (node)
"A depth first approach for printing out all values in a tree."
(when (node-data node)
(format t "~a " (node-data node)))
(loop for child in (node-children node) do
(dfs-recursive child)))
(defun dfs-recursive-postorder (node)
"A depth first approach for printing out all values in a tree starting from the bottom."
(loop for child in (node-children node) do
(dfs-recursive-postorder child))
(when (node-data node)
(format t "~a " (node-data node))))
(defun dfs-recursive-inorder-btree (node)
"A depth first search approach for printing all values in a binary tree."
(case (length (node-children node))
(2
(dfs-recursive-inorder-btree (first (node-children node)))
(format t "~a " (node-data node))
(dfs-recursive-inorder-btree (second (node-children node))))
(1
(dfs-recursive-inorder-btree (first (node-children node)))
(format t "~a " (node-data node)))
(0
(format t "~a " (node-data node)))
(t
(print "Invalid binary tree."))))
(defun dfs-stack (node)
"A depth first approach for printing out all values in a tree using a stack."
(loop
with stack = (list node)
with temp = nil
while (> (length stack) 0) do
(format t "~a " (node-data (first stack)))
(setf temp (pop stack))
(loop for child in (node-children temp) do
(push child stack))))
(defun bfs-queue (node)
"A breadth first search approach for printing out all values in a tree."
(loop
with queue = (list node)
with temp = nil
while (> (length queue) 0) do
(format t "~a " (node-data (first queue)))
(setf temp (pop queue))
;; If the queue is empty, the queue should be filled with the children nodes.
(if (eql queue nil)
(setf queue (node-children temp))
(nconc queue (node-children temp)))))
(defun make-tree (num-rows num-child)
"Creates a simple tree, where every node has 'num-child' children and is 'num-rows' deep."
;; A tree with 0 rows can't be created.
(if (eql num-rows 0)
(make-node
:data 0
:children nil)
(make-node
:data num-rows
:children (loop repeat num-child collect (make-tree (1- num-rows) num-child)))))
;; A tree for testing
(defvar tree (make-tree 2 3))
;; A binary tree for testing
(defvar binary-tree (make-tree 3 2))
;; Should print: 3 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 1
(format t "[#]~%Recursive DFS:~%")
(dfs-recursive tree)
(format t "~%")
;; Should print: 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 3
(format t "[#]~%Recursive Postorder DFS:~%")
(dfs-recursive-postorder tree)
(format t "~%")
;; Should print: 3 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 1
(format t "[#]~%Stack-based DFS:~%")
(dfs-stack tree)
(format t "~%")
;; Should print: 3 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
(format t "[#]~%Queue-based BFS:~%")
(bfs-queue tree)
(format t "~%")
;; Should print: 1 2 1 3 1 2 1
(format t "[#]~%Recursive Inorder DFS for Binary Tree:~%")
(dfs-recursive-inorder-btree binary-tree)
(format t "~%")
main()
%% Functions
function root = create_tree()
node = @(k,v) containers.Map(k,v);
node2 = node(2, {{}}); node3 = node(3, {{}}); node4 = node(4, {{}});
node6 = node(6, {{}}); node7 = node(7, {{}}); node8 = node(8, {{}});
node10 = node(10, {{}}); node11 = node(11, {{}}); node12 = node(12, {{}});
node1 = node(1, {node2, node3, node4});
node5 = node(5, {node6, node7, node8});
node9 = node(9, {node10, node11, node12});
root = node(0, {node1, node5, node9});
end
function root = create_btree()
node = @(k,v) containers.Map(k,v);
node2 = node(2, {{}}); node3 = node(3, {{}});
node5 = node(5, {{}}); node6 = node(6, {{}});
node1 = node(1, {node2, node3});
node4 = node(4, {node5, node6});
root = node(0, {node1, node4});
end
function DFS_recursive(n)
cell_index = @(a, b) a{b};
ID = cell_index(keys(n), 1);
fprintf('%u ', ID);
children = cell_index(values(n), 1);
for i = children
child = i{1};
if ~isempty(child)
DFS_recursive(child);
end
end
end
function DFS_recursive_postorder(n)
cell_index = @(a, b) a{b};
children = cell_index(values(n), 1);
for i = children
child = i{1};
if ~isempty(child)
DFS_recursive_postorder(child);
end
end
ID = cell_index(keys(n), 1);
fprintf('%u ', ID);
end
function DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(n)
cell_index = @(a, b) a{b};
ID = cell_index(keys(n), 1);
children = cell_index(values(n), 1);
if length(children) == 2
DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(children{1})
fprintf('%u ', ID)
DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(children{2})
elseif length(children) == 1
if ~isempty(children{1})
DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(children{1})
end
fprintf('%u ', ID)
else
fprintf("Not a binary tree!")
end
end
function DFS_stack(n)
cell_index = @(a, b) a{b};
node_stack = {n};
while ~isempty(node_stack)
parent = node_stack{end};
node_stack(end) = [];
ID = cell_index(keys(parent), 1);
fprintf('%u ', ID);
children = cell_index(values(parent), 1);
for i = flip(children)
child = i{1};
if ~isempty(child)
node_stack = {node_stack{:} child};
end
end
end
end
function BFS_queue(n)
cell_index = @(a, b) a{b};
node_queue = {n};
while ~isempty(node_queue)
next_nodes = {};
for parent_cell = node_queue
parent = parent_cell{1};
ID = cell_index(keys(parent), 1);
fprintf('%u ', ID);
children = cell_index(values(parent), 1);
for i = children
child = i{1};
if ~isempty(child)
next_nodes = {next_nodes{:}, child};
end
end
end
node_queue = next_nodes;
end
end
function main()
root = create_tree();
rootb = create_btree();
fprintf('\nDFS Recursive\n')
DFS_recursive(root)
fprintf('\nDFS Recursive Postorder\n')
DFS_recursive_postorder(root)
fprintf('\nDFS Recursive Inorder Binary Tree\n')
DFS_recursive_inorder_btree(rootb)
fprintf('\nDFS Stack\n')
DFS_stack(root)
fprintf('\nBFS Queue\n')
BFS_queue(root)
fprintf('\n')
end
from collections import deque
data Node(value: int, children: Node[])
def dfs_recursive(Node(value, children)):
"""A depth first approach for printing out all values in a tree."""
print(value, end=' ')
for child in children:
dfs_recursive(child)
def dfs_recursive_postorder(Node(value, children)):
"""A depth first approach for printing out all values in a tree starting from the bottom."""
for child in children:
dfs_recursive_postorder(child)
print(value, end=' ')
def dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(Node(value, children)):
"""A depth first search approach for printing all values in a binary tree."""
match len(children):
case 2:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(children[0])
print(value, end=' ')
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(children[1])
case 1:
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(children[0])
print(value, end=' ')
case 0:
print(value, end=' ')
else:
print('Invalid binary tree')
def dfs_stack(Node(node)):
"""A depth first approach for printing out all values in a tree using a stack."""
stack = [node]
while stack:
current_node = stack.pop()
print(current_node.value, end=' ')
for child in current_node.children:
stack.append(child)
def bfs_queue(Node(node)):
"""A breadth first search approach for printing out all values in a tree."""
queue = deque([node])
while queue:
current_node = queue.popleft()
print(current_node.value, end=' ')
for child in current_node.children:
queue.append(child)
def create_tree(num_rows, num_child):
"""Creates a simple tree, where every node has
'num_child' children and is 'num_rows' deep."""
if num_rows == 0:
return Node(0, ())
else:
return Node(num_rows, tuple(create_tree(num_rows-1, num_child)
for _ in range(num_child)))
if __name__ =='__main__':
# A ternary tree for testing
tree = create_tree(2, 3)
print("[#]\nRecursive DFS:")
dfs_recursive(tree)
print()
print("[#]\nRecursive Postorder DFS:")
dfs_recursive_postorder(tree)
print()
print("[#]\nStack-based DFS:")
dfs_stack(tree)
print()
print("[#]\nQueue-based BFS:")
bfs_queue(tree)
print()
# And a binary tree for testing
binary_tree = create_tree(3, 2)
print("[#]\nRecursive Inorder DFS for Binary Tree:")
dfs_recursive_inorder_btree(binary_tree)
print()
License
Code Examples
The code examples are licensed under the MIT license (found in LICENSE.md).
Text
The text of this chapter was written by James Schloss and is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Images/Graphics
- The image "DFSpreorder" was created by James Schloss and is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The image "DFSpostorder" was created by James Schloss and is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The image "DFSinorder" was created by James Schloss and is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The image "BFSsimple" was created by James Schloss and is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Pull Requests
After initial licensing (#560), the following pull requests have modified the text or graphics of this chapter:
- none